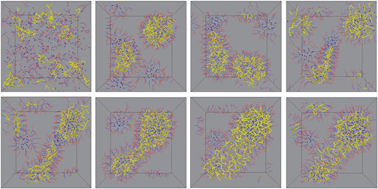
We carried out molecular dynamics simulations to investigate the morphological change of water-in-oil microemulsion (ME) droplets by addition of polymer chains. Several experiments have shown an increase in the polydispersity of ME droplet size and the morphological transition of spherical ME droplets to a rod-like shape by encapsulating the polymer chain in ME droplets. In order to understand these changes in the ME droplets, we studied the effects of the chain concentration and the interaction strength between chains and surfactant. When the interaction strength was weak, we obtained spherical droplets rather than rod-like droplets. Two types of spherical ME droplets were observed: large spherical droplets containing polymer chains and small spherical droplets without chains, which resulted in a large size polydispersity. However, when the interaction strength was great, a coalescence of ME droplets containing polymer chains was observed and the morphology of the droplets finally changed to a rod-like shape with an increase in the chain concentration. The morphological change can be explained by the competition between the chain–surfactant interaction energy and the surfactant monolayer bending energy, thus the interaction energy prefers a rod-like shape to gain a large contact area between the chains and the surfactant monolayer.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...