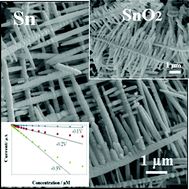
Tin nanodendrites have been fabricated using galvanic replacement reaction between stannous chloride (SnCl2) and thermal evaporated zinc film composed of Zn nanodiscs. The replacement reaction is completed in a few seconds, and the produced Sn nanodendrites possess a single crystalline structure. The growth process of Sn nanodendrites is studied by changing the concentration of SnCl2 in the replacement reaction, and the growth direction is identified by electron diffraction analysis. The as-prepared Sn nanodendrites are further oxidized by rheotaxial growth and thermal oxidation (RGTO) process to generate tin oxide nanodendrites. The electrochemical properties of SnO2 nanodendrites are demonstrated in the electrocatalytic reaction of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), and the reduction of H2O2 is tremendously enhanced in terms of the onset potential and the magnitude of reduction current. The amperometric H2O2 sensor, using the as-prepared SnO2 nanodendrites as the electrochemical catalyst, shows a wide linear range, a good limit of detection, a high sensitivity, and good reproducibility. This study provides a promising route to the facile synthesis of functional metals/metal oxides with unusual nanostructures, which have great potential in sensing applications.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...