Novel nanostructured pHEMA–TiO2 hybrid materials with efficient light-induced charge separation
Abstract
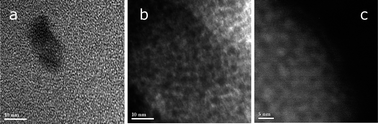
We report on a new approach to the fabrication of an electronic material: organic–inorganic pHEMA–oxo-TiO2 hybrid with efficient light-induced separation of charges. Particular attention is paid to the material nanoscale morphology. The size-selected 5.0 nm titanium oxo-alkoxy

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...