Photophoretic assembly and migration of dielectric particles and Escherichia coli in liquids using a subwavelength diameter optical fiber†
Abstract
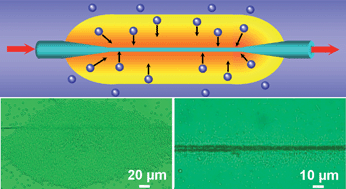
We demonstrate a photophoretic assembly and migration of dielectric (SiO2 and TiO2) particles and bacteria (Escherichia coli) in liquids by using a subwavelength diameter fiber. With a lightwave at 1.55 μm launched into the fiber, the objects are radiated by the leaking light of the fiber to yield negative photophoretic forces which drive the objects to move toward the fiber, with an average assembling/migrating speed of 5–15 individuals per second (ind/s). The influences of laser-on duration, optical power, and size of particles on the photophoretic velocities are also investigated.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...