DNA nanofabrication by scanning near-field photolithography of oligo(ethylene glycol) terminated SAMs: Controlled scan-rate dependent switching between head group oxidation and tail group degradation
Abstract
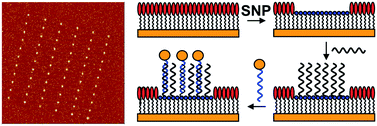
The use of scanning near-field photolithography (SNP) to fabricate DNA
- This article is part of the themed collection: Materials Chemistry of Nanofabrication

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...