K0.46Na0.54NbO3 ferroelectric ceramics: chemical synthesis, electro-mechanical characteristics, local crystal chemistry and elastic anomalies
Abstract
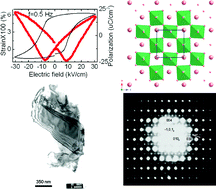
K0.46Na0.54NbO3 ceramics have been fabricated via a chemical synthesis route. It was found that 500 °C heat treatment is sufficient to crystallize the niobate powder and the ceramic sintered at 1080 °C in air shows good ferroelectric and piezoelectric properties (Pr ∼ 15 μC cm−2, d33 ∼ 120 pC N−1). Electron diffraction patterns not only determine the space group symmetry of Pcm21 for the first time, but also reveal structural disorder in K0.46Na0.54NbO3, and 1-D correlated strings of Nb–O atomic displacements are suggested to account for the polar behaviour. Elastic constants such as the bulk and shear moduli as well as their evolution with temperature were also measured using the resonant ultrasound

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...