Stereochemical effects of chiral monolayers on enhancing the resistance to mammalian cell adhesion†
Abstract
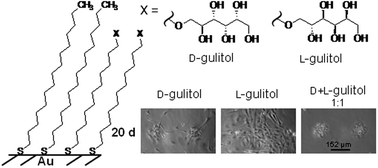
This work describes the different durations of surface confinement of adhered mammalian cells by monolayers comprised of enantiomers of bio-inert

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...