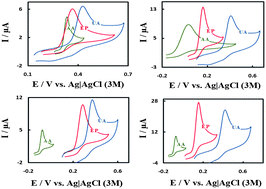
The development of a highly selective sensor for voltammetric determination of ascorbic acid (AA), epinephrine (EP) and uric acid (UA) in the same solution has been achieved by a glassy carbon electrode modified with multi-walled carbon nanotubes and ruthenium oxide hexacyanoferrate film. The modified electrode showed effective catalytic activity toward the electro-oxidation of AA, EP and UA by separating their oxidation peak potentials and producing larger anodic peak currents than those at unmodified electrodes. The electron transfer efficiency and rate constant of the oxidation process were studied using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. The electro-catalytic peak currents of differential pulse voltammograms increased linearly with AA, EP and UA concentrations in the ranges of 0.2–15.0 μM, 0.1–10.0 μM and 0.90–250 μM with a detection limit of 0.087, 0.052 and 0.599 μM, respectively. The modified electrode showed good sensitivity, selectivity and stability for the voltammetric determination of these important biological compounds. The modified electrode was satisfactorily used for simultaneous determination of AA, EP and UA in pharmaceutical and biological samples.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...