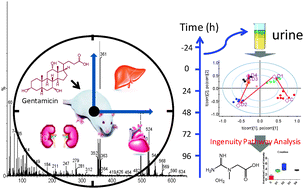
We introduce the use of Ingenuity Pathway Analysis to analyzing global metabonomics in order to characterize phenotypically biochemical perturbations and the potential mechanisms of the gentamicin-induced toxicity in multiple organs. A single dose of gentamicin was administered to Sprague Dawley rats (200 mg/kg, n = 6) and urine samples were collected at −24–0 h pre-dosage, 0–24, 24–48, 48–72 and 72–96 h post-dosage of gentamicin. The urine metabonomics analysis was performed by UPLC/MS, and the mass spectra signals of the detected metabolites were systematically deconvoluted and analyzed by pattern recognition analyses (Heatmap, PCA and PLS-DA), revealing a time-dependency of the biochemical perturbations induced by gentamicin toxicity. As result, the holistic metabolome change induced by gentamicin toxicity in the animal's organisms was characterized. Several metabolites involved in amino acid metabolism were identified in urine, and it was confirmed that gentamicin biochemical perturbations can be foreseen from these biomarkers. Notoriously, it was found that gentamicin induced toxicity in multiple organs system in the laboratory rats. The proof-of-knowledge based Ingenuity Pathway Analysis revealed gentamicin induced liver and heart toxicity, along with the previously known toxicity in kidney. The metabolites creatine, nicotinic acid, prostaglandin E2, and cholic acid were identified and validated as phenotypic biomarkers of gentamicin induced toxicity. Altogether, the significance of the use of metabonomics analyses in the assessment of drug toxicity is highlighted once more; furthermore, this work demonstrated the powerful predictive potential of the Ingenuity Pathway Analysis to study of drug toxicity and its valuable complementation for metabonomics based assessment of the drug toxicity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...