Structural, electrochemical, phosphate-hydrolysis, DNA binding and cleavage studies of new macrocyclic binuclear nickel(ii) complexes†
Abstract
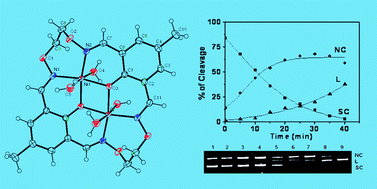
New macrocyclic binuclear nickel(II) complexes have been synthesized by using the bicompartmental mononuclear complex [NiL] [3,30-((1E,7E)-3,6-dioxa-2,7-diazaocta-1,7-diene-1,8-diyl)bis(3-formyl-5-methyl-2-diolato)nickel(II)] with various diamines like 1,2-bis(aminooxy)ethane (L1), 1,2-diamino ethane (L2), 1,3-diamino propane (L3), 1,4-diamino butane (L4), 1,2-diamino benzene (L5), and 1,8-diamino naphthalene (L6). The complexes were characterized by elemental analysis and spectroscopic methods. The molecular structures of the symmetrical binuclear complex [Ni2L1(H2O)4](ClO4)2 (1) and unsymmetrical binuclear complex [Ni2L3(H2O)4](ClO4)2·(H2O)4 (3) were determined by single-crystal X-ray diffraction. The geometry around both the nickel(II) ions in each molecule is a slightly distorted octahedral. The distance between the Ni⋯Ni centers for complex 1 is 3.039 Å and for complex 3 is 3.059 Å. The influence of the coordination geometry and the ring size of the binucleating ligands on the electronic, redox, phosphate hydrolysis, DNA binding and cleavage properties have been studied. Electrochemical studies of the complexes show two quasi-reversible one electron reduction processes between −0.49 to −1.69 V. The reduction potential of the binuclear Ni(II) complexes shifts towards anodically upon increasing the macrocyclic ring size. The observed first order rate constant values for the hydrolysis of 4-nitrophenyl phosphate reaction are in the range from 8.69 × 10−3 to 1.85 × 10−2 s−1. The complexes show good binding propensity to calf thymus DNA giving binding constant values in the range from 1.4 × 104 to 17.5 × 104 M−1. The absorption, fluorescence and CD spectral data suggests that the complexes are strongly interacting with DNA. These complexes display hydrolytic cleavage of supercoiled pBR322DNA in the presence of H2O2 at pH 7.2 and 37 °C. The hydrolytic cleavage of DNA by the complexes is supported by the evidence from free radical quenching and T4 ligase ligation. The pseudo-Michaelis–Menten kinetic parameters kcat = 1.27 ± 0.4 h−1 and KM = 7.7 × 10−2 M for naphthalene diimine containing macrocyclic binuclear nickel(II) complex, (6) were obtained.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...