Electrochemical study of dopamine and noradrenaline at the water/1,6-dichlorohexane interface†
Abstract
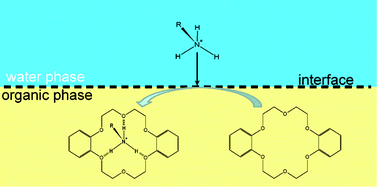
Interfaces between two immiscible electrolyte solutions are recognized as a simplified model for biological systems and they can be of great relevance to the characterization of biomolecules and their role in biological systems. In this work, ion transfer and facilitated ion transfer of protonated catecholamines (
- This article is part of the themed collection: Electrified surface chemistry

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...