Photophysical pathways of cytosine in aqueous solution†
Abstract
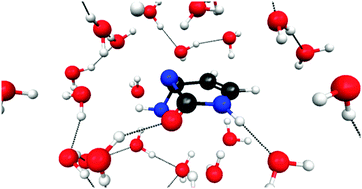
The effects of aqueous solvation on the photophysical pathways involving the S1 excited state in
- This article is part of the themed collection: Molecular mechanisms of the photostability of life

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...