Tyrosine-67 in cytochrome c is a possible apoptotic trigger controlled by hydrogen bonds via a conformational transition†
Abstract
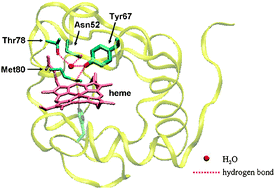
We found that cyt c Y67H and Y67R variants represent a state which resembles the conformational intermediate state in cyt c with high

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...