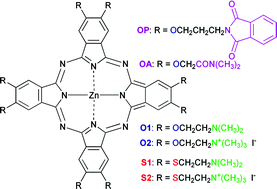
This work describes a systematic comparison of oxygen and sulfur as covalent linkers on octasubstituted zinc(II) phthalocyaninates. Most photophysical parameters that make phthalocyanines technologically relevant, e.g. molar absorption coefficients, fluorescence, triplet and singlet oxygen quantum yields, are essentially unaffected by the substitution. The energy content of the first triplet state was observed to be close to the first singlet state of molecular oxygen for both spacers, as follows from photoacoustic determinations. Nonetheless, a bathochromic shift of 30 nm in the absorption and emission maxima, and of 60 nm in the triplet–triplet absorption spectra were observed when alkyloxyl and alkylsulfanyl moieties were alternatively present. Fluorescence quantum yields proved to be much more sensitive towards aggregation than the absorption spectra. Therefore, a novel fluorescence data analysis provided aggregation parameters and photophysical properties of the monomeric species. It was observed that the tendency towards dimerization is slightly higher with sulfur linkers. These results set a foundation for the rational design of conveniently substituted phthalocyaninates with different connectors between the macrocycle and the side chains.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...