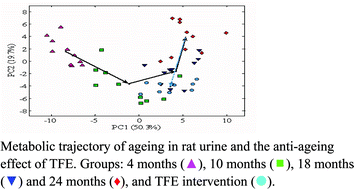
The aim of this work was to investigate the effects of ageing on rat urinary metabolites and to evaluate the anti-ageing effects of the total flavone of Epimedium (TFE). Proton nuclear magnetic resonance based metabonomic analyses was performed on urine from rats aged 4, 10, 18 and 24 months, and rats administered with TFE. By multivariate analysis, 26 characteristic resonances were found to be highly related with the age of rats, and ten of them were structurally postulated as creatinine, lactate, alanine, acetate, acetone, succinate, allantoin, methylamine, dimethylamine and trimethylamine-N-oxide; these metabolites involve creatininemetabolites, aliphatic amines metabolites and some important intermediates or end products of energy metabolism. Principal components analysis revealed that the metabolic profiles of 24-month-old rats treated with TFE closely resembled those of rats aged 18 months. In addition, most of these characteristic resonances were reset to younger levels by TFE intervention. The result suggests that TFE administration can markedly influence the ageing process and shows anti-ageing effects, which might due to the melioration of pyruyate metabolism and oxidative phosphorylation.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...