Synthesis and near-infrared luminescence of a deuterated conjugated porphyrin dimer for probing the mechanism of non-radiative deactivation
Abstract
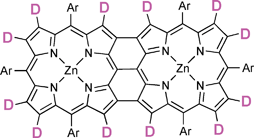
β,meso,β-Fused
* Corresponding authors
a
Department of Chemistry, Chemistry Research Laboratory, University of Oxford, 12 Mansfield Road, Oxford, UK
E-mail:
harry.anderson@chem.ox.ac.uk
Fax: +44 1865-28-5002
Tel: +44 1865 275744
b
Molecular Photoscience Group, Istituto per la Sintesi Organica e la Fotoreattività, Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche, Via Gobetti 101, Bologna, Italy
E-mail:
armaroli@isof.cnr.it
c Air Force Research Laboratory, AFRL/MLPJ, 3005 Hobson Way, Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, Dayton, Ohio, USA
d Defence Science and Technology Laboratory, St Andrews Road, Malvern, UK
β,meso,β-Fused

 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
M. J. Frampton, G. Accorsi, N. Armaroli, J. E. Rogers, P. A. Fleitz, K. J. McEwan and H. L. Anderson, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2007, 5, 1056 DOI: 10.1039/B700408G
To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content.
 Fetching data from CrossRef.
Fetching data from CrossRef.
This may take some time to load.
Loading related content
