α- and β-Stilbenosides as base-pair surrogates in DNA hairpins†
Abstract
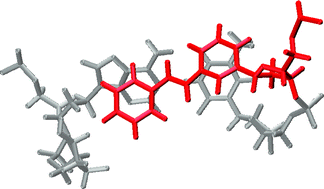
The synthesis, structure, and optical spectroscopy of hairpin oligonucleotide conjugates possessing synthetic stilbene C-nucleosides (stilbenosides) are reported. Synthetic methods for selective preparation of both the α- and β-stilbenosides have been developed. Both anomers are effective in stabilizing hairpin structures when used as capping groups at the open end of the hairpin base-pair domain. However, only the β-anomer effectively stabilizes the hairpin structure when located in the interior of the base-pair domain opposite an abasic site. Similar results are obtained for hairpins possessing two stilbenosides, either adjacent to each other or with one intervening base-pair. Molecular dynamics simulations are employed to obtain averaged structures for these conjugates. The calculated structures for the capped hairpins formed with either anomer show effective π-stacking with the adjacent base-pair. The calculated structures for the internal stilbenosides show that the α- and β-anomers form extrahelical and intrahelical structures, respectively. The relative orientations of the two stilbenes in the bis-stilbenosides have been studied using a combination of exciton-coupled circular dichroism spectroscopy and molecular modeling.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...