HCl and DCl: A case study of different approaches for determining photo fractionation constants
Abstract
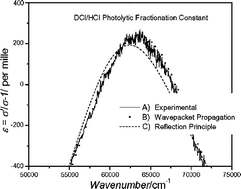
The photoabsorption cross sections of HCl and DCl are calculated using the reflection principle and time dependent wavepacket propagation methods. The absorption cross sections are compared to high precision experimental absorption cross sections from the literature and the different results given by the methods are discussed. The results of the calculations emphasize the important roles that photodissociation dynamics and the change in transition dipole moment with internuclear distance play in isotopic

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...