Li2O–B2O3–GeO2 glass as a high performance anode material for rechargeable lithium-ion batteries†
Abstract
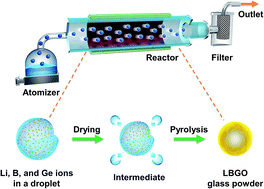
Group IV metal oxides, such as GeO2, SiOx, and SnO2, have been considered promising anode materials of lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) because of their significantly higher specific capacities than those of their conventional graphite counterparts. These metal oxides, however, suffer from immense volume variations and aggregation of active domains, resulting in inferior cycle lives of batteries. Herein, we report lithium-ion conducting Li2O–2B2O3–2GeO2 glass as a new LIB anode material by employing fast spray pyrolysis (residence time ∼ 10 s). Spray pyrolysis allows the formation of spherical particles with a narrow diameter range and homogeneous mixing of the individual glass components. Taking advantage of lithium-ion conductivity through inter-domain pathways as well as the Li2O–2B2O3 glass phase that alleviates the volume expansion and aggregation of GeO2 active phases, the LBGO glass electrode exhibited a high reversible capacity of 881.1 mA h g−1 along with 92.7% capacity retention after 150 cycles when measured at 1.0 A g−1. The present study opens a new avenue for developing high capacity LIB electrode materials, that is, lithium-ion conducting glass materials that can avoid volume expansion and the aggregation of active domains via buffering glass matrices.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2018 Journal of Materials Chemistry A HOT Papers


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...