Insight into the structural and electronic nature of chemically exfoliated molybdenum disulfide nanosheets in aqueous dispersions†
Abstract
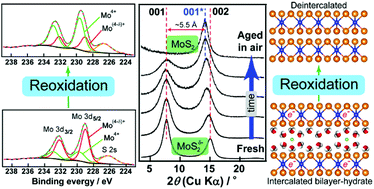
Chemical exfoliation of molybdenum disulfide (2H-MoS2) for preparing high-yield single-layer sheets has attracted considerable attention in recent years. However, the stability and nature of the resulting nanosheets are poorly understood. Storing the dispersion in ambient air brings about the reoxidation of the nanosheets, releasing their residual negative charges into the environment. The reoxidation facilitates lateral fractures and destabilizes the dispersion. In-plane X-ray diffraction of the nanosheets indicates that they have a 1T structure with a 2D √3 × 1 rectangular cell as the intrinsic structure for chemically exfoliated MoS2. We found that the 1T structure was preserved after reoxidation upon aging the dispersions in air, suggesting the formation of metastable neutral MoS2. The changes in the chemical nature of the nanosheets can be monitored by X-ray diffraction of the restacked nanosheets. The restacked nanosheets, obtained by drying the freshly prepared dispersion, exhibited an expanded bilayer hydrate structure, accommodating Li ions. On the other hand, dried samples from the aged dispersions were substantially composed of a deintercalated phase and the bilayer hydrate. Upon prolonged aging, the former phase became predominant with total disappearance of the latter. This evolution suggests that the reoxidation occurred sheet by sheet with a direct restoration of the original oxidation states of the nanosheets, whereas the oxidation states of the nanosheets can be discrete at 4+ and (4 − δ)+.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Recent Developments in Intercalation Compounds: Chemistry and Applications


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...