High-resolution synchrotron terahertz investigation of the large-amplitude hydrogen bond librational band of (HCN)2†
Abstract
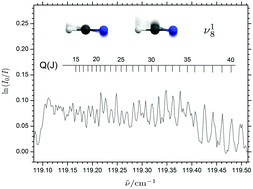
The high-resolution terahertz absorption spectrum of the large-amplitude intermolecular donor librational band ν18 of the homodimer (HCN)2 has been recorded by means of long-path static gas-phase Fourier transform spectroscopy at 207 K employing a highly brilliant electron storage ring source. The rovibrational structure of the ν18 band has the typical appearance of a perpendicular type band of a Σ–Π transition for a linear polyatomic molecule. The generated terahertz spectrum is analyzed employing a standard semi-rigid linear molecule Hamiltonian, yielding a band origin ν0 of 119.11526(60) cm−1 together with values for the excited state rotational constant B′, the excited state quartic centrifugal distortion constant DJ′ and the l-type doubling constant q for the degenerate state associated with the ν18 mode. The until now missing donor librational band origin enables the determination of an accurate experimental value for the vibrational zero-point energy of 2.50 ± 0.05 kJ mol−1 arising from the entire class of large-amplitude intermolecular modes. The spectroscopic findings are complemented by CCSD(T)-F12b/aug-cc-pV5Z (electronic energies) and CCSD(T)-F12b/aug-cc-pVQZ (force fields) electronic structure calculations, providing a (semi)-experimental value of 17.20 ± 0.20 kJ mol−1 for the dissociation energy D0 of this strictly linear weak intermolecular CH⋯N hydrogen bond.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2018 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...