Magnetic Fe3O4@polyaniline nanocomposites with a tunable core–shell structure for ultrafast microwave-energy-driven reduction of Cr(vi)†
Abstract
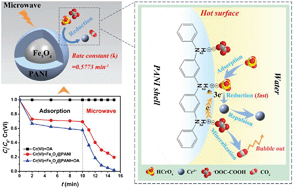
Magnetic core–shell Fe3O4@polyanilines (Fe3O4@PANI) were controllably synthesized to harvest microwave (MW) energy for ultrafast Cr(VI) reduction. The nanocomposites are excellent MW acceptors due to the combination of the magnetic loss of Fe3O4 and dielectric loss of PANI. Under MW irradiation, abundant hot spots are generated on Fe3O4@PANI to accelerate the reduction of surface-bound Cr(VI). Moreover, Fe3O4@PANI is highly stable in an acidic solution and readily recoverable with an external magnet after use. The PANI shell possesses good enrichment ability for Cr(VI), creating a high Cr(VI) surface concentration which benefits the sequential reduction. Furthermore, an increase in the PANI coating amount from 24.78% to 55.15% increases the Cr(VI) adsorption capacity (qe) from 0.63 mmol g−1 to 1.68 mmol g−1, which linearly enhances the removal rate constant (k) of Cr(VI) under an MW field as k = 0.30qe − 0.03. The addition of oxalic acid as a sacrificial electron donor increases the Cr(VI) removal rate by 120.09% and protects the PANI shell from excessive oxidation by Cr(VI); this prolongs the lifetime of Fe3O4@PANI. In the presence of oxalic acid, the MW-driven Cr(VI) reduction on Fe3O4@PANI proceeds at a rate constant of 0.5773 min−1, which is much higher than that of palladium-based chemocatalysis. Moreover, Fe3O4@PANI can be in situ regenerated by MW and directly reused in the next cycle, and no efficiency loss occurs in 5 continuous runs. The mechanism study based on Cr species tracking and solid analyses indicates that a synergistic adsorption and reduction cycle proceed consecutively, contributing to the rapid Cr(VI) removal. This study demonstrates that Fe3O4@PANI is a promising alternative to utilize MW for ultrafast Cr(VI) reduction and has the advantages of time-saving and energy efficiency.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...