Development of a novel parallel determination platform: a feasibility study tested on a chemiluminescence device
Abstract
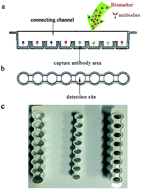
The potential of obtaining incremental diagnostic information using a parallel assay is attractive. Herein, a novel parallel determination platform was developed for the simultaneous determination of hormones, including human growth hormone (GH), prolactin (PRL), thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). Polystyrene was used as a support material and the device comprised an antibody capture area, a connecting channel, and an isolating bar. After immobilizing antibodies in the antibody capture area, 50 μL antigens and 1.5 mL of HRP-labelled antibodies were mixed and bound to the capture antibodies by flowing in the connecting channel continually. After adding chemiluminescence substrates, the isolating bar enabled the connecting channel to enter into the detection site in a 1 : 1 ratio. Fluorescein isothiocyanate-labelled bovine serum albumin (FITC-BSA) was used as an internal standard. The developed method was validated in terms of limits of detection (LOD), linearity, recovery and precision. The LOD were 0.01 mIU L−1, 0.01 IU L−1, 0.03 mIU L−1, 0.05 mIU L−1, and 0.01 IU L−1 for GH, FSH, TSH, PRL, and LH, respectively. The assay was linear up to 230 mIU L−1 for GH (r2 = 0.995), 300 IU L−1 for FSH (r2 = 0.991), 100 mIU L−1 for TSH (r2 = 0.997), 8000 mIU L−1 for PRL (r2 = 0.994), and 260 IU L−1 for LH (r2 = 0.992). The mean recoveries were calculated at two concentration levels and the values were found to be between 90.5% and 108.3%. The intra- and inter-assay coefficients of variation were <10% and <11%, respectively. The method was successfully applied to determine serum sample (n = 120) and the results were strongly correlated with the Siemens and Abbott immunoassay, showing a bias offset of 1.7 mIU L−1, 2.4 IU L−1, 0.1 mIU L−1, 7.6 mIU L−1 and 1.5 IU L−1 for GH, FSH, TSH, PRL, and LH. This sensitive and cost-efficient platform is expected to be a powerful tool to measure combinations of various biomarkers.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...