Synthesis of ultra-small carbon nanospheres (<50 nm) with uniform tunable sizes by a convenient catalytic emulsion polymerization strategy: superior supercapacitive and sorption performance†
Abstract
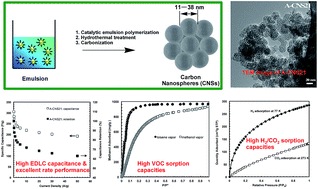
Porous carbon nanospheres have received enormous attention due to their various applications. Although several elegant strategies exist for the synthesis of relatively large carbon nanospheres (>ca. 100 nm), the synthesis of carbon nanospheres with well-defined, tunable ultra-small sizes (<50 nm) has often been challenging, while such ultra-small nanospheres are much more valuable. A novel, convenient and scalable catalytic emulsion polymerization technique is demonstrated in this paper for the highly efficient synthesis of ultra-small carbon nanospheres with uniform tunable sizes in the range of 11–38 nm. In this strategy, a simple change in the emulsion polymerization recipe renders a convenient yet efficient tuning of the size of the carbon nanospheres. In particular, activated carbon nanospheres (A-CNS21 with an average size of 21 nm), obtained by carbonization in the presence of KOH as the chemical activation agent, possess a very high surface area (2360 m2 g−1) and desired hierarchical macro-/meso-/micropore structures which result from nanosphere packing/aggregation. A-CNS21 is demonstrated to exhibit superior high-rate supercapacitive performance and outstanding sorption capacities towards volatile organic compounds (VOCs), H2 and CO2, which are comparable to or even better than the best results reported to date in these applications. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first synthesis of ultra-small carbon nanospheres, with uniform tunable sizes and superior performance for these applications, by the emulsion polymerization strategy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...