Ultra-small iron-gallic acid coordination polymer nanoparticles for chelator-free labeling of 64Cu and multimodal imaging-guided photothermal therapy†
Abstract
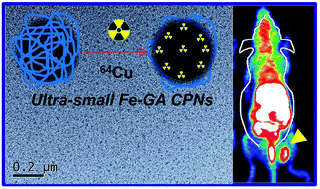
Cancer nanotechnology has become the hot topic nowadays. While various kinds of nanomaterials have been widely explored for innovative cancer imaging and therapy applications, safe multifunctional nano-agents without long-term retention and toxicity are still demanded. Herein, iron-gallic acid coordination nanoparticles (Fe-GA CPNs) with ultra-small sizes are successfully synthesized by a simple method for multimodal imaging-guided cancer therapy. After surface modification with polyethylene glycol (PEG), the synthesized Fe-GA-PEG CPNs show high stability in various physiological solutions. Taking advantage of high near-infrared (NIR) absorbance as well as the T1-MR contrasting ability of Fe-GA-PEG CPNs, in vivo photoacoustic tomography (PAT) and magnetic resonance (MR) bimodal imaging are carried out, revealing the efficient passive tumor targeting of these ultra-small CPNs after intravenous (i.v.) injection. Interestingly, such Fe-GA-PEG CPNs could be labeled with the 64Cu isotope via a chelator-free method for in vivo PET imaging, which also illustrates the high tumor uptake of Fe-GA CPNs. We further utilize Fe-GA-PEG CPNs for in vivo photothermal therapy and achieve highly effective tumor destruction after i.v. injection of Fe-GA-PEG CPNs and the following NIR laser irradiation of the tumors, without observing any apparent toxicity of such CPNs to the treated animals. Our work highlights the promise of ultra-small iron coordination nanoparticles for imaging-guided cancer therapy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...