pLoc-mPlant: predict subcellular localization of multi-location plant proteins by incorporating the optimal GO information into general PseAAC†
Abstract
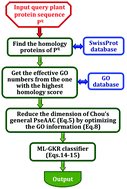
One of the fundamental goals in cellular biochemistry is to identify the functions of proteins in the context of compartments that organize them in the cellular environment. To realize this, it is indispensable to develop an automated method for fast and accurate identification of the subcellular locations of uncharacterized proteins. The current study is focused on plant protein subcellular location prediction based on the sequence information alone. Although considerable efforts have been made in this regard, the problem is far from being solved yet. Most of the existing methods can be used to deal with single-location proteins only. Actually, proteins with multi-locations may have some special biological functions. This kind of multiplex protein is particularly important for both basic research and drug design. Using the multi-label theory, we present a new predictor called “pLoc-mPlant” by extracting the optimal GO (Gene Ontology) information into the Chou's general PseAAC (Pseudo Amino Acid Composition). Rigorous cross-validation on the same stringent benchmark dataset indicated that the proposed pLoc-mPlant predictor is remarkably superior to iLoc-Plant, the state-of-the-art method for predicting plant protein subcellular localization. To maximize the convenience of most experimental scientists, a user-friendly web-server for the new predictor has been established at http://www.jci-bioinfo.cn/pLoc-mPlant/, by which users can easily get their desired results without the need to go through the complicated mathematics involved.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...