Differential α-amylase/α-glucosidase inhibitory activities of plant-derived phenolic compounds: a virtual screening perspective for the treatment of obesity and diabetes†
Abstract
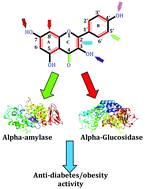
Recently, due to their biological properties, polyphenol-rich functional foods have been proposed to be unique supplementary and nutraceutical treatments for diabetes mellitus. Inhibition of α-amylase and α-glucosidase enzymes using natural products (especially polyphenols) is a novel oral policy to regulate carbohydrate metabolism and hyperglycemia. The present study aims to evaluate the α-amylase and α-glucosidase inhibitory activity of 26 polyphenols using molecular docking and virtual screening studies. The results speculate that among selected compounds caffeic acid, curcumin, cyanidin, daidzein, epicatechin, eridyctiol, ferulic acid, hesperetin, narenginin, pinoresinol, quercetin, resveratrol and syringic acid can significantly inhibit the α-glucosidase enzyme. In addition, catechin, hesperetin, kaempferol, silibinin and pelargonidin are potent α-amylase inhibitors. Therefore the primary structure of polyphenols can change the inhibitory effect versus the α-amylase and α-glucosidase enzymes. Finally, we speculate that consumption of polyphenol-rich functional foods (by considering the best dose of each compound and assessing their possible side effects) in diabetic patients may be useful for regulating carbohydrate metabolism and related disorders. The findings of the current study may also shed light on a way of generating a new class of amylase/glucosidase inhibitors that will discriminately inhibit the on-target enzymes with negligible undesired off-target side effects.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...