Metal–support interactions in catalysts for environmental remediation
Abstract
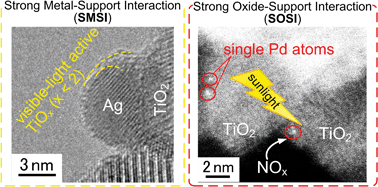
Catalytic decomposition of organic air pollutants is attractive in environmental remediation but challenging because such a reaction must take place at ambient temperature. To achieve sufficient catalytic activity under these conditions, the size, morphology and electric state of catalysts are critical. In particular, the interaction between noble metals and their ceramic supports is crucial for these catalysts. Herein we elucidate the significance of strong metal–support interactions (SMSIs) and strong oxide–support interactions (SOSIs) in such catalysts. The SMSIs lead to embedded metal nanoparticles into ceramic supports, hindering metal particle growth. For example, SMSIs in Pt–TiO2 formed by reduction of NaBH4 at room temperature allows stabilization of Pt clusters of 1–2 nm in diameter. On the other hand, SMSIs in Ag–TiO2 composites form crystalline TiOx (x < 2) that is a highly active photocatalyst under the full range of visible light (400–800 nm). Furthermore, such embedded structures could enhance visible light absorption by plasmonic materials. The SOSIs take place between metals and supports through oxygen ligands forming their hetero-bimetallic structure (e.g. Cu–O–Ti). This enables absorption of visible light and facilitates the transfer of photo-excited electrons to the co-catalysts (e.g. TiO2 to Cu), resulting in superior visible-light activity with a quantum yield of over 50%. Also, such interactions allow stabilization of small metal clusters and even single atoms on the supports to significantly facilitate the catalytic oxidation of pollutants at ambient temperature. For example, single Pd atoms on TiO2 increase its photocatalytic NOx removal by 9 times while only doubling its cost.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...