In situ investigation on Co-phase evolution and its performance for Fischer–Tropsch synthesis over Nb-promoted cobalt catalysts†
Abstract
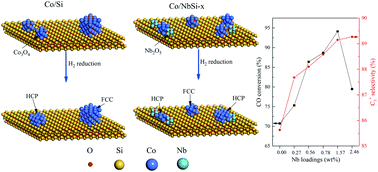
Nb-promoted cobalt catalysts were prepared by the incipient wetness impregnation method and characterized by ex/in situ XRD, in situ DRIFTS, N2 physisorption, TEM, EDS-mapping, H2-TPR, CO/H2-TPD, and XPS. Their performance was investigated in a fixed bed reactor for Fischer–Tropsch synthesis (FTS). As regards the sample texture, niobium oxide (NbOx) can obviously reduce the BET surface area and pore volume, and promote the formation of uniform cobalt particles with a smaller size. The presence of NbOx complexes can weaken the metal–support interaction, while it also makes Co3O4 species easily reducible to metallic cobalt and favours the formation of a hexagonal close-packed cobalt phase, as confirmed by the results of H2-TPR and ex/in situ XRD. What's more, NbOx can enhance the adsorption stability and the amount of CO adsorbed under approximately actual FTS reaction conditions, as verified by the results of CO-TPD. In addition, NbOx complexes can be considered as weak electron donors, as confirmed by the results of XPS, leading to a higher concentration of surface carbon species. According to the performance results, the selectivity to C5+ products increased to 89.3% from 85.6% and the CO conversion was significantly increased to 94.1% from 70.7% with the increase of Nb loading to 1.57 wt% from zero. It is found that highly selective production of heavy hydrocarbons can be achieved at a higher activity level over Nb-promoted cobalt catalysts.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2017 Catalysis Science & Technology HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...