The influence of polyanion molecular weight on polyelectrolyte multilayers at surfaces: elasticity and susceptibility to saloplasticity of strongly dissociated synthetic polymers at fluid–fluid interfaces
Abstract
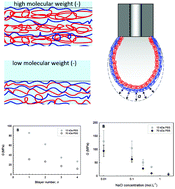
We studied the interfacial mechanical properties of polyelectrolyte multilayer assemblies of poly(diallylamine hydrochloride) (PAH) and poly(4-styrenesulfonate)sodium salt (PSS) at the air–water interface using axisymmetric drop shape analysis (ADSA) during hydrostatic inflation as a function of aqueous salt concentration and two different polyanion molecular weights (Mw ∼ 13 and 70 kDa). Surface elastic moduli (Gs) ranged from 50 to 300 mN m−1. Using the measured film thickness, the bulk moduli (G) ranged from 10 to 90 MPa consistent with elastomeric solids. This solid-like interface was evidenced by a systematic departure of the inflated shape from the Young–Laplace equation, which assumes a liquid-like interface. Surface elastic moduli increased and bulk elastic moduli decreased with increasing nanomembrane transverse dimension, and multilayers with the lower molecular weight anion were more transversely compact than those of higher molecular weight and displayed a larger elastic modulus. The bulk moduli of both types of multilayer assemblies asymptotically approach a constant value for films with more than two bilayers of polyelectrolyte, consistent with the observed transition from a ’glassy‘ to ‘rubbery’ state. Both types of multilayer assemblies displayed plasticization with increasing sodium chloride concentration in the adjoining aqueous phase, i.e. saloplasticity, and exhibited a transition from elastic to plastic response to deformation. The restored mobility of the polyelectrolyte resulting from the shift from intrinsic to extrinsic charge complexation, restores fluidity to the interface and is evidenced by experimental observation of a liquid-like interface when loaded. The higher molecular weight polyanion multilayers plasticized at lower salt concentrations suggesting that the lower melting point of the higher molecular weight polyanion assembly is attributable to a lesser extent of electrostatic cross-linking underscoring the unconventional dependence of molecular weight on saloplasticity in strongly dissociated polyelectrolytes.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Surface chemistry and interface science


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...