Effect of Co co-doping on the optical properties of ZnTe:Mn nanocrystals
Abstract
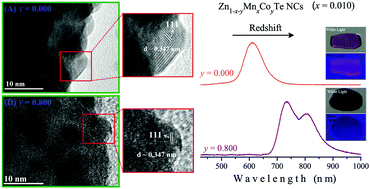
We study the effect of Co co-doping on the optical properties of Mn-doped ZnTe nanocrystals (NCs) embedded in a glass matrix. Optical absorption (OA) and crystal field theory strongly indicated the substitutional incorporation of Co2+ ions into these semiconducting NCs as well as the characteristic transitions of these ions in the visible and near infrared spectral region. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images revealed an invariant NC lattice parameter with the incorporation of Mn2+ and Co2+ ions. The same was confirmed by X-ray diffraction (XRD). The photoluminescence (PL) spectra showed that the characteristic emission bands of Co2+ ions (E1Co2+ and E2Co2+) are intense and evident at low temperatures. Indeed, Raman spectra showed that the dependence of luminescence intensity on temperature is due to the electron–phonon interaction that arises from multiphonon relaxation processes. The redshifts in the PL spectra from green to orange with the incorporation of Mn2+ ions into ZnTe NCs, and in the near infrared with increasing Co-concentration, result from sp–d exchange interactions associated with the increase in Mn2+ and Co2+ ions in tetrahedral sites of ZnTe NCs, which may be very interesting for applications in luminescent devices. These observations provide strong evidence that higher Co-concentrations inhibit the incorporation of Mn2+ into ZnTe NCs, suggesting that there may be competition between Co2+ and Mn2+ ions substituting Zn2+ ions and, furthermore, that these ions replace zinc vacancies (VZn) in these NCs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...