Review – trace determination of potentially toxic elements in (medicinal) plant materials
Abstract
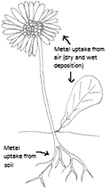
Medicinal herbs are nowadays widely used as home remedies for a huge variety of ailments. As non-synthetic medicines, they are considered safe for human health. Due to metal uptake from soil via roots, from air via wet or dry deposition or by contamination during processing, plant materials may contain high amounts of harmful metals, such as arsenic, cadmium or lead. The World Health Organization (WHO) has thus established maximum concentration limits for these elements in order to ensure the safe use of herbs. Therefore, it is important to determine the current metal levels in herbs and their parts used for medical applications in order to determine any potential contamination. These concentrations are in the trace and ultra-trace range; thus analytical experience is needed for appropriate sampling, sample preparation, subsequent measurement by a suitable method and finally the evaluation and interpretation of the data obtained. In the presented review, possible sample preparation methods as well as analytical methods suitable for the given analytical task are summarized and discussed. Based on the sample matrix, the metals to be determined and their expected concentration range, and the sample preparation method as well as the subsequent analytical instrument have to be carefully chosen, optimized and validated.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...