Carbon nanospheres derived from Lablab purpureus for high performance supercapacitor electrodes: a green approach†
Abstract
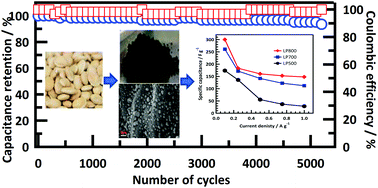
Carbon nanospheres derived from a natural source using a green approach were reported. Lablab purpureus seeds were pyrolyzed at different temperatures to produce carbon nanospheres for supercapacitor electrode materials. The synthesized carbon nanospheres were analyzed using SEM, TEM, FTIR, TGA, Raman spectroscopy, BET and XRD. They were later fabricated into electrodes for cyclic voltammetry, galvanostatic charge/discharge and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy testing. The specific capacitances were found to be 300, 265 and 175 F g−1 in 5 M KOH electrolyte for carbon nanospheres synthesized at 800, 700 and 500 °C, respectively. These are on a par with those of prior electrodes made of biologically derived carbon nanospheres but the cycle lives were remarkably higher than those of any previous efforts. The electrodes showed 94% capacitance retention even after 5200 charge/discharge cycles entailing excellent recycling durability. In addition, the practical symmetrical supercapacitor showed good electrochemical behaviour under a potential window up to 1.7 V. This brings us one step closer to fabricating a commercial green electrode which exhibits high performance for supercapacitors. This is also a waste to wealth approach based carbon material for cost effective supercapacitors with high performance for power storage devices.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...