High performance near-infrared photodetectors based on ultrathin SnS nanobelts grown via physical vapor deposition†
Abstract
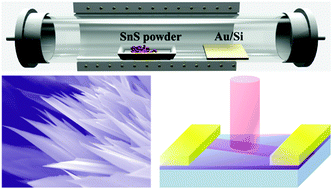
Ultrathin SnS nanobelts were synthesized via physical vapor deposition (PVD). Furthermore, high performance near-infrared (NIR) photodetectors based on SnS nanobelts showed an excellent photoresponsivity of 300 A W−1 under 800 nm light illumination with an external quantum efficiency of 4.65 × 104% and a detectivity of 6 × 109 Jones, as well as fast rise and decay times (τrise = 36 ms and τdecay = 7 ms), suggesting a promising future for the utilization of the SnS nanobelts in practical NIR light sensors.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2016 Journal of Materials Chemistry C Hot Papers

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...