Novel 1.5 V anode materials, ATiOPO4 (A = NH4, K, Na), for room-temperature sodium-ion batteries†
Abstract
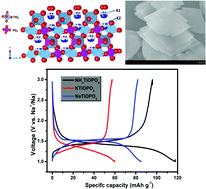
Due to the abundance of sodium in nature, sodium-ion batteries (SIBs) have attracted widespread attention. Numerous intercalated cathode materials have already been reported, but fewer intercalated anode materials are known. Among these materials, most anodes suffer from low coulombic efficiency and the dendritic growth of sodium due to the lower sodiated voltages (below 1.0 V). To improve the safety performance of batteries, exploring new anode materials which have higher sodiated voltage above 1.0 V is very important. Herein, a series of novel intercalated anode materials, ATiOPO4 (A = NH4, K, Na), is introduced for SIBs at the first time. Preparation of NaTiOPO4 by a traditional solid-state reaction is difficult. So we first synthesized NH4TiOPO4 (NTP) by a simple hydrothermal reaction, KTiOPO4 (KTP) and NaTiOPO4 (NaTP) were each prepared by ion exchange with the respective nitrate. These samples were investigated by electrochemical discharge/charge which showed average sodiated voltages of 1.45 V (NTP), 1.4 V (KTP) and 1.5 V (NaTP); respectively. In situ XRD results indicated that a two-phase reaction mechanism accompanies electrochemical Na insertion/extraction in NaTP. These anode materials are potential candidates for developing SEI-free and high safety SIBs.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2016 Journal of Materials Chemistry A HOT Papers

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...