A one-step electrodeposition of homogeneous and vertically aligned nanotubes with parahydrophobic properties (high water adhesion)†
Abstract
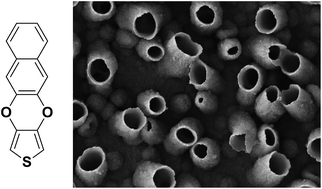
Here, we report for the first time parahydrophobic (high water adhesion) vertically aligned nanotubes by a one-step electropolymerization of naphtho[2,3-b]thieno[3,4-e][1,4]dioxine (NaphDOT) without surfactants and hard templates. The formation of nanotubes is probably due to the stabilization by the polymer of gas bubbles produced in situ during the electropolymerization process. The nanotubes are obtained by cyclic voltammetry or at constant potential, but their formation is highly dependent on the deposition method. From cyclic voltammetry it was found that the size of the nanotubes is extremely large (∅ ≈ 300 nm) and independent of the number of deposition scans, while only the density of nanotubes increases. At constant potential, all the seeds for the nanotube formation are created in the first moments, while the size of the nanotube increases with the deposition charge. Here, θw values up to 135° are obtained even if the polymer is intrinsically highly hydrophilic (Young's angle θY = 63.6°). Moreover, water droplets put on these substrates remain stuck even after an inclination of 90° revealing extremely high adhesion. Such materials could be used in water transportation and harvesting, energy systems and biosensing.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2016 Journal of Materials Chemistry A HOT Papers

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...