Bacterial degradation of crude oil using solid formulations of bacillus strains isolated from oil-contaminated soil towards microbial enhanced oil recovery application
Junhui Zhanga,
Quanhong Xue*a,
Hui Gaoa,
Hangxian Laia and
Ping Wangb
aCollege of Natural Resources and Environment, Northwest A & F University, 3 Taicheng Road, Yangling 712100, China. E-mail: xuequanhong@163.com; Fax: +86-29-87080055; Tel: +86-29-87044264
bCollege of Earth Sciences and Resources, Chang'an University, Xi'an 710055, China
First published on 7th January 2016
Abstract
Microbial enhanced oil recovery has played a major role in enhancing crude oil recovery from depleted oil reservoirs to solve stagnant petroleum production. Most studies have focused on the use of bacteria by liquid-state fermentation, with less attention paid to solid-state fermentation. Here, we examined the efficiency of crude oil degradation using solid formulations of Bacillus strains and evaluated their feasibility for application in enhanced oil recovery. Three Bacillus strains, namely B. atrophaeus 5-2a, B. aryabhattai 6-2a and B. amyloliquefaciens 6-2c, were isolated from oil-contaminated soil samples. Two strains, 5-2a and 6-2c, secreted extracellular biosurfactants with excellent oil-displacing and emulsifying activity; their diameter of clear zone and emulsification index were 19.7–20.1 cm and 56.6–61.1%, respectively. Three bacterial formulations demonstrated high efficiency to degrade resins (max 24.18%) and asphaltene (max 56.17%), and they decreased the viscosity of crude oil to varying degrees at 40 °C (max 26.47%). The associated CO2 and H2 production was 33.0–36.2 mmol L−1 and 61.8–68.0 mmol L−1, respectively, and acid production was 1410–1560 mg L−1. Bacterial formulations removed 82.32–94.50% of crude oil adsorbed on filter paper in 4 d at 40 °C. The results indicate that the three bacterial formulations are efficient in degrading and removing crude oil.
Introduction
It is urgent to improve crude oil production to meet the global energy demands. Conventional oil extraction can recover less than half of an oil reservoir, and nearly two-thirds of crude oil still is trapped in the rock pores.1–3 As the petroleum reserves directly available shrinks, it is necessary to exploit profoundly the oil resources from existing and marginal reservoirs. Therefore, increasing attention has been focused on chemical enhanced oil recovery to mobilize entrapped oil from the existing and abandoned oilfields.3,4 Chemical methods are claimed to have significant potential based on successful laboratory testing; however, the results in field trials have not been encouraging. Furthermore, chemical processes are expensive and complex operational, leaving non-biodegradable residues potentially toxic to the environment.5,6Microbial enhanced oil recovery (MEOR) is emerging as a cost-effective, environmental-friendly, and potentially efficient approach to improve oil production.7–9 In the process of MEOR, microbial formulations are inoculated into a reservoir, allowing microbial population and/or associated metabolic products to pose certain beneficial effects, such as formation of oil–water emulsions, decrease of interfacial tension between oil and water, increase of permeability, and mobilization of residual oil.10,11 Bacillus strains inhabiting oil-contaminated soils presumably are able to utilize hydrocarbon and tolerate the reservoir conditions. For instance, the genus Bacillus can survive and produce desirable MEOR formulations when grown on glucose mineral salts medium.12 B. subtilis PTCC 1365,13 B. subtilis PT2 (ref. 14) and B. licheniformis ACO1 (ref. 15) isolated from oil-contaminated soils recovered 22–60% of the residual oil entrapped in sand-packed columns.
Microorganisms can enhance the recovery of residual oil by excreting metabolic byproducts including biosurfactants, emulsifiers, biopolymers, solvents and acids.1,16 Biosurfactants was able to alter oil/water/rock interfacial properties, thereby leading to enhanced oil recovery.3,11 Biosurfactant flooding as a green and promising methods has been extensively studied.17,18 The production of acids (e.g., acetic, propionic acids, and butyric acid) helps dissolve carbonates, thereby increasing the permeability and porosity of limestone reservoirs.3 Additionally, gas production has been mentioned as an important mechanism for oil recovery, since gas products (e.g., CO2, H2, and CH4) can improve the mobility of oil by reducing its viscosity and re-pressurizing the reservoir.19 Moreover, bacteria can selectively plug high permeability channels and thereby improve volumetric sweep efficiency, as has been studied by nutrient resuscitation and growth of starved cells in sandstone cores.20,21
There are three strategies commonly used to implement MEOR: (1) injection of selected nutrients to stimulate the growth of indigenous microorganisms in a reservoir, (2) injection of exogenous microorganisms and nutrients, allowing for colonization of microorganisms in situ, and (3) injection of ex situ produced products.4,22 The first two approaches are more favorable from an economic point of view; however, they require specific microorganisms that can survive and produce large amounts of metabolic byproducts in a reservoir. The third strategy is the simplest and thus most likely to succeed at the field-scale. However, the use of liquid formulations has added the difficulty in transporting and storing microbial agents for a long term. To address this problem, we proposed to prepare bacterial formulations through solid-state fermentation. Such advanced MEOR based on the use of solid formulations of bacterial agents may prove effective and successful in oil production.
The aim of this study was to assess the efficiency of solid formulations for bacterial degradation of crude oil. Three Bacillus strains were obtained from oil-contaminated surface soils in an oilfield. Bacterial formulations were prepared through solid-state fermentation. After bacterial degradation, changes in the physicochemical properties of crude oil were assessed in terms of crude oil fraction degradation, oil viscosity, oil removal, and gas-acid production. This study provides evidence for the feasibility of using solid formulations in MEOR.
Results and discussion
Identification of bacterial cultures
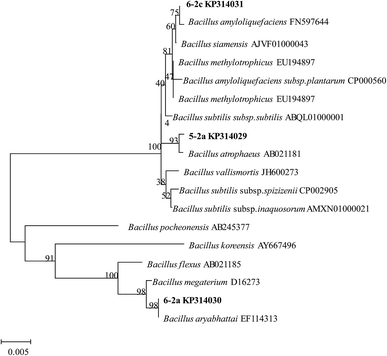
Three pure bacterial cultures, designated as 5-2a, 6-2a, and 6-2c, were isolated from oil-contaminated soil samples, all of which could utilize crude oil as the sole carbon source. Based on morphological (Fig. 1 and 2) and sequencing analysis (Fig. 3), these pure cultures were identified as B. atrophaeus (5-2a), B. aryabhattai (6-2a), and B. amyloliquefaciens (6-2c). GenBank accession numbers to their sequences are KP314029 (5-2a), KP314030 (6-2a), and KP314031 (6-2c). Solid formulations from these Bacillus strains were named B1 (B. atrophaeus 5-2a), B2 (B. aryabhattai 6-2a), and B3 (B. amyloliquefaciens 6-2c).Bacterial degradation of crude oil fractions
The efficiency of bacterial formulations B1 to B3 to degrade various fractions of crude oil is shown in Table 1. Percentages of degradation after 4 d of incubation were 12.46–15.09% for saturates, 23.89–39.26% for aromatics, 19.78–24.18% for resins, and 53.09–56.17% for asphaltenes present in crude oil. The current results are higher than the efficiency of bacterial consortia to degrade aromatics (0–18%) and asphaltenes (4–20%), and close to the upper limit for resins (6–29%) present in crude oil, as illustrated by Sugiura et al.,28 Tehrani et al.,29 and Zhang et al.30 A number of compounds slightly degradable by microorganisms are contained in the fractions of resins and asphaltenes. Resins and asphaltenes are high-molecular-weight and strongest polar components of crude oil that are difficult to be degraded, which results in the difficulty of oil recovery.30 The current bacterial formulations with high degradation efficiency for the resin and asphaltene fractions may be useful for improving the flow properties of crude oil.| Formulations | Saturates | Aromatics | Resins | Asphaltenes | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mg 2 g−1) | VRm% | (mg 2 g−1) | VRm% | (mg 2 g−1) | VRm% | (mg 2 g−1) | VRm% | |
| a Oil fractions are mean ± standard deviation (n = 3). Different letters within a column indicate significant differences (P < 0.05) according to Duncan's multiple range test. Ctrl for control; VRm% for bacterial degradation-associated variations in the mass of four crude oil fractions. | ||||||||
| Ctrl | 1027 ± 5a | — | 540 ± 6a | — | 91 ± 3a | — | 162 ± 1a | — |
| B1 | 899 ± 6b | 12.46 | 336 ± 4c | 37.78 | 71 ± 1b | 21.98 | 76 ± 2b | 53.09 |
| B2 | 889 ± 4b | 13.44 | 328 ± 6c | 39.26 | 73 ± 1b | 19.78 | 72 ± 2b | 55.56 |
| B3 | 872 ± 6c | 15.09 | 411 ± 3b | 23.89 | 69 ± 5b | 24.18 | 71 ± 3b | 56.17 |
The relative variations in total number and peak area of gasifiable n-alkanes at 240 °C are shown in Table 2. The three formulations caused progressive increases in the total number of gasifiable n-alkanes by 6.67% (B1) to 33.33% (B3). Correspondingly, the total peak area of gasifiable n-alkanes was increased by 62.64% (B1) to 107.99% (B3). These results demonstrate the strong ability of solid formulations B1 to B3 to degrade n-alkanes into lighter fractions under extreme oxygen-deprived conditions. Numerous bacterial genera have been identified as hydrocarbon-degrading microorganisms, including Bacillus species such as B. thermoleovorans and B. subtilis.2,31 Felix and Cooney32 reported that spore-forming bacteria generally have a major role in oil biodegradation. These bacteria can transform heavier fractions into lighter fractions to decrease the viscosity and enhance the flow characteristics of crude oil.
| No. | Retention time (min) | Ctrl | B1 | B2 | B3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peak area | VRa% | Peak area | VRa% | Peak area | VRa% | |||
| a Note: VRa% for bacterial degradation-associated variations in chromatographic peak area of each n-alkane at different retention times. | ||||||||
| 1 | 15.813 | 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 525 525 |
19![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 863 863 |
88.72 | 36![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 989 989 |
251.44 | 42![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 218 218 |
301.12 |
| 2 | 18.113 | 20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 859 859 |
31![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 249 249 |
49.81 | 46![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 363 363 |
122.27 | 51![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 271 271 |
145.80 |
| 3 | 20.275 | 24![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 158 158 |
34![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 366 366 |
42.26 | 40![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 363 363 |
67.08 | 47![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 917 917 |
98.35 |
| 4 | 22.338 | 26![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 328 328 |
36![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 593 593 |
38.99 | 39![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 164 164 |
48.75 | 46![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 748 748 |
77.56 |
| 5 | 24.275 | 23![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 045 045 |
32![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 714 714 |
41.96 | 32![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 605 605 |
41.48 | 39![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 608 608 |
71.87 |
| 6 | 26.138 | 19![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 523 523 |
33![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 829 829 |
73.28 | 31![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 288 288 |
60.26 | 39![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 361 361 |
101.61 |
| 7 | 27.900 | 20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 116 116 |
33![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 394 394 |
66.01 | 30![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 103 103 |
49.65 | 36![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 807 807 |
88.53 |
| 8 | 29.575 | 24![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 824 824 |
37![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 147 147 |
49.64 | 32![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 759 759 |
31.97 | 39![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 377 377 |
58.62 |
| 9 | 31.188 | 23![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 649 649 |
38![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 531 531 |
62.93 | 32![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 886 886 |
39.06 | 38![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 699 699 |
63.64 |
| 10 | 32.725 | 25![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 795 795 |
38![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 162 162 |
47.94 | 33![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 963 963 |
31.67 | 41![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 402 402 |
60.50 |
| 11 | 34.213 | 24![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 129 129 |
36![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 583 583 |
51.61 | 31![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 570 570 |
30.84 | 39![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 996 996 |
65.76 |
| 12 | 35.638 | 25![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 833 833 |
38![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 539 539 |
49.19 | 32![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 761 761 |
26.82 | 41![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 612 612 |
61.08 |
| 13 | 37.275 | 28![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 055 055 |
43![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 649 649 |
55.58 | 32![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 026 026 |
14.15 | 42![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 999 999 |
53.27 |
| 14 | 39.300 | 19![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 010 010 |
34![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 404 404 |
80.98 | 27![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 578 578 |
45.07 | 32![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 361 361 |
70.23 |
| 15 | 41.863 | 15![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 355 355 |
24![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 725 725 |
61.02 | 20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 558 558 |
33.88 | 26![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 475 475 |
71.77 |
| 16 | 21.575 | 0 | 13![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 267 267 |
14![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 734 734 |
18![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 451 451 |
— | ||
| 17 | 13.388 | 0 | 0 | 26![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 068 068 |
27![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 871 871 |
— | ||
| 18 | 26.238 | 0 | 0 | 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 596 596 |
13![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 065 065 |
— | ||
| 19 | 10.850 | 0 | 0 | 11![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 651 651 |
10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 677 677 |
— | ||
| 20 | 17.500 | — | — | — | 12![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 001 001 |
— | ||
| ∑ | 331![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 200 200 |
538![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 665 665 |
62.64 | 564![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 024 024 |
70.30 | 688![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 868 868 |
107.99 | |
Biosurfactant production and crude oil removal efficiency
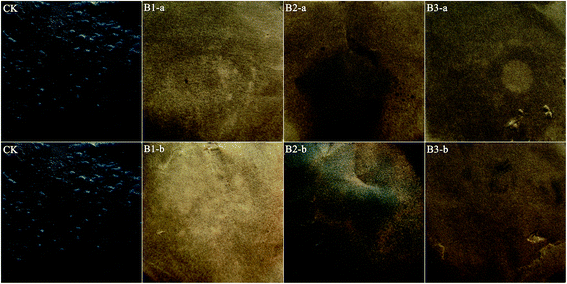
Biosurfactant production was assayed by using the oil spreading test and emulsifying activity determination. According to Youssef et al.,25 the diameter of a clear zone is directly proportional to the concentration of a biosurfactant. In the current study, crude bacterial biosurfactants from strains 5-2a and 6-2c exhibited strong oil-spreading activity. Their diameter of oil spreading from cell-free culture both reached 19.7–20.1 cm, that is, 3.0-fold that of the control; the emulsification indices were between 56.6% and 61.1%. The oil-spreading activity of strain 6-2a was weak, as indicated by a small diameter (7.9 cm) of clear zone and a lack of emulsifying activity.Moreover, crude oil removal test was used to evaluate the removal efficiency of the bacterial formulations. All the three formulations removed the majority of crude oil adsorbed on filter paper (Fig. 4). The removal efficiency of bacterial formulations ranged from 82.32% (B2) to 94.50% (B3), that is, 7.32–8.40-fold that of the control. During the recycled use, crude oil removal efficiency relatively decreased but still reached 71.78–92.65%, that is, 6.38–8.24-fold that of the control (Table 3).
| Formulations | Viscosity (Pa s) | VRR% | Fresh formulation suspension | Recycled formulation suspension | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RE% | REs/REck | RE% | REs/REck | |||
| a Values are mean ± standard deviation (n = 3). Different letters within a column indicate significant differences (P < 0.05) according to Duncan's multiple range test. VRR% for viscosity reduction rate; RE% for crude oil removal efficiency. | ||||||
| Ctrl | 23.8 ± 0.3a | — | 11.25 ± 0.19c | — | 11.25 ± 0.19c | — |
| B1 | 17.7 ± 0.8b | 25.63 | 94.50 ± 0.21a | 8.40 | 92.65 ± 0.042a | 8.24 |
| B2 | 18.5 ± 0.5b | 22.27 | 82.32 ± 0.13b | 7.32 | 71.78 ± 0.092b | 6.38 |
| B3 | 17.5 ± 0.5b | 26.47 | 94.20 ± 0.21a | 8. 37 | 92.47 ± 0.14a | 8.22 |
In MEOR, biosurfactants are able to reduce the interfacial tension and alter the wettability of reservoir rock for water-flood to displace more oil from the capillary network.11 Our results show that formulations B1 and B3 exhibit markedly higher ability to produce biosurfactants and remove crude oil compared with Bacillus strains in sand pack column studies (30.22–34.19% oil recovery)33 and a consortium of Enterobacter cloacae and Pseudomonas sp. (27.2% oil recovery).34 Therefore, B. atrophaeus 5-2a (B1) and B. amyloliquefaciens 6-2c (B3) have promising potential for use in MEOR.
Changes in crude oil viscosity
The high viscosity of crude oil is one of the major factors responsible for poor oil recovery from producing wells and it prevents the migration of oil through the rock pores within the reservoir.1,3 In the present study, all the three formulations decreased oil viscosity to varying degrees at 40 °C due to bacterial degradation (Table 3). B3 showed higher efficiency (26.47%) to decrease oil viscosity than B1 (25.63%) and B2 (22.27%). The decreases in oil viscosity by Bacillus formulations are in agreement with previous findings about bacterial strains such as Rhodococcus ruber Z25 (ref. 35) and B. subtilis.2 The ability of three B. subtilis strains to degrade oil and decrease oil viscosity provides a mechanism to enhance the mobility and increase the production of oil in a reservoir.Gas production from bacterial degradation of crude oil
During the process of crude oil degradation by bacterial formulations, a considerable amount of gases was produced. The gas products mainly included CO2 (∼35%) and H2 (∼65%), with the production of 33.0–36.2 and 61.8–68.0 mmol L−1, respectively. The total gas production was 94.8–104.2 mmol L−1 and the gas production rate was 212.3–233.3% (Table 4).| Formulations | Gas production (mmol L−1) | Gas production rate GPR% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | CO2 | H2 | ||
| a Gas production is mean ± standard deviation (n = 3). Different letters within a column indicate significant differences (P < 0.05) according to Duncan's multiple range test. | ||||
| Ctrl | 0 ± 0.0d | 0 ± 0.0d | 0 ± 0.0d | 0 |
| B1 | 94.8 ± 1.5c | 33.0 ± 0.5c | 61.8 ± 1.0c | 212.3 |
| B2 | 99.3 ± 1.5b | 34.5 ± 0.6b | 64.7 ± 1.0b | 222.3 |
| B3 | 104.2 ± 1.0a | 36.2 ± 0.4a | 68.0 ± 0.7a | 233.3 |
Gas, as a product of microbial activity in MEOR, can improve the mobility of oil by reducing the oil viscosity and re-pressurizing the reservoir.1,3,36 The current study shows that the solid formulations of three Bacillus strains are able to promote high levels of CO2 and H2 production, which can benefit oil recovery from depleted reservoirs. Oil recovery studies have detected comparable large amounts of gas in reservoir with favorable results where microorganisms were injected.19 Bacillus species are the most common microorganisms used for gas production in MEOR processes. Spore production by these species is also beneficial because spores survive harsh conditions and penetrate deep into the petroleum reservoir.36 Therefore, the three biogas-producing strains obtained in the present study would be promising microorganisms for use in MEOR.
Acid production from bacterial degradation of crude oil
Laboratory experiments have shown that the efficiency of MEOR depends on the ability of microorganisms to grow and produce metabolites such as solvents, acids, gases, and biosurfactants.3,8 Acids (e.g., acetic, propionic acids, and 1-butanoic acid) can dissolve carbonates and thereby increase the permeability and porosity of oil reservoir.3 In the present study, substantial acids were produced during bacterial degradation of crude oil. The total acid number was within the range of 1410–1560 mg L−1, while the pH of reaction solutions decreased by 26.47–36.03% compared to the control (Table 5).| Formulations | pH | Acid production | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measurements | pH reduction rate RR% | Total acidity TA (mmol L−1) | Total acid number TAN (mg L−1) | |
| a Values are mean ± standard deviation (n = 3). Different letters within a column indicate significant differences (P < 0.05) according to Duncan's multiple range test. | ||||
| Ctrl | 6.80 ± 0.025a | — | 0.0 ± 0.0a | 0 |
| B1 | 5.00 ± 0.029b | 26.47 | 23.5 ± 0.7b | 1410 |
| B2 | 4.49 ± 0.016c | 33.97 | 25.5 ± 0.7c | 1530 |
| B3 | 4.35 ± 0.016d | 36.03 | 26.0 ± 0.0d | 1560 |
The total acid numbers for crude oil degradation by B1 to B3 were nearly 2.6-fold that reported for a mixed culture of Thermoanaerobacter (540 mg L−1) grown at 70 °C with molasses as carbon source.37 Additionally, certain bacterial cultures, such as a bacterium consortium of Enterobacter Cloacae and Enterobacter hormaechei, can barely cause a real and significant change in the pH during fermentation.38,39 Together these results highlight that bacterial formulations obtained in the present study can promote high levels of acid production when breaking down crude oil.
Liquid chromatography showed that the organic acids produced by bacterial degradation of crude oil mainly comprised oxalate, formate, and propionate. Since oxalate (a dicarboxylic acid), formate and propionate (a carboxylic acid) have strong acid strength, all of these acids have the potential of dissolving carbonate rocks to increase permeability and porosity. This mechanism would contribute to increasing crude oil fluidity and thereby enhancing crude oil recovery.
Conclusions
Three Bacillus strains were isolated from oil-contaminated surface soil. Two isolates were selected as high biosurfactant producers, both of which exhibited desirable oil-spreading activity and emulsifying activity. Solid formulations from these bacterial cultures exhibited excellent activities for crude oil degradation, including degradation of resin and asphaltene fractions, reduction of oil viscosity, and production of gases and organic acids. Given their convenient storage, transportation and use, these solid formulations have the potential for application in MEOR. This study establishes a new approach for the development of solid formulations of bacterial agents towards MEOR application. Future investigations should test the feasibility of B1 to B3 for field application, for example, using laboratory-scale sand-pack columns.Materials and methods
Media, crude oil, and soil
Crude oil and soil samples were collected in the Ansai oilfield, Shaanxi Province, Northwest China. An oil sample was obtained from a low permeability reservoir (Hua-20-4). Oil-contaminated soil samples were obtained in the vicinity of kowtow machines and oil tanks near wells Hua-119 and Hao-129. Details on the source of oil and soil samples are available in our recent publication.23The basal mineral salt medium (MSM) contained (g L−1): NaNO3 2.0, (NH4)2SO4 1.0, MgSO4·7H2O 0.3, KH2PO4 5.0, K2HPO4·3H2O 5.0, and NaCl 5.0, with pH adjusted to 7.0. The enrichment and isolation media were prepared by supplementing MSM with 2% (v/v) crude oil as the sole carbon source. The fermentation medium contained (g L−1): beef extract 3.0, peptone 10.0, NaCl 5.0, and brown sugar 10.0, with pH adjusted to 7.0. The solid formulation-producing medium contained MSM, wheat bran, and crude oil (60![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 100
100![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2, v/g/g). All regents were of analytical grade.
2, v/g/g). All regents were of analytical grade.
Bacterial isolation and identification
Soil enrichment cultures were prepared in 250 mL glass bottles containing 100 mL of enrichment medium supplemented. Ten grams of soil samples were weighed into each bottles and then incubated at 30 °C in the dark for 5 d. The cultures (5 mL each) were subsequently passaged to fresh enrichment medium three times. Aliquots (50 μL) of the fourth-generation enrichment cultures were spread on oil plates of the isolation medium and incubated at 30 °C under aerobic conditions.Morphologically distinct colonies were picked and purified by streaking on fresh fermentation medium plates at least three times. Three pure bacterial cultures, designated as 5-2a, 6-2a, and 6-2c, were obtained and identified by morphological examination and gene sequencing.2 The purified cultures were maintained on beef extract peptone agar and deposited in the China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) under the accession numbers CCTCC M 2014673 (5-2a), CCTCC AB 2015004 (6-2a), and CCTCC M 2015740 (6-2c).
Preparation of solid formulations and bacterial suspensions
Single colonies of each bacterial culture were transferred to 100 mL of fermentation medium, incubated at 30 °C with shaking (120 rpm) for 3 d to obtain a cell density of 1010 colony-forming unit per milliliter (CFU mL−1). The seed inoculum with 20% (v/v) was transferred into 50 g of solid formulation-producing medium and grown for 5 d at 30 °C. Thereafter, medium containing Bacillus strains was air-dried to 30% moisture content and then oven-dried at 40 °C for 48 h. The dry material was ground into powder and passed through a 0.10 mm sieve to obtain a powder formulation. The solid formulations from Bacillus strains 5-2a, 6-2a, and 6-2c were named B1 to B3 and their viable counts were 9.5 × 1010, 12.0 × 1010 and 35.3 × 1010 CFU g−1, respectively. The formulations were stored at room temperature until use.The prepared formulations and distilled water were blended 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3 in glass bottles. The suspensions were incubated at 30 °C with shaking (120 rpm) for 0.5 h and then filtered through sterile cotton wool to obtain bacterial cell suspensions.
3 in glass bottles. The suspensions were incubated at 30 °C with shaking (120 rpm) for 0.5 h and then filtered through sterile cotton wool to obtain bacterial cell suspensions.
Crude oil degradation
Crude oil (2 g each) was prepared in 100 mL glass bottles containing 30 mL of bacterial suspension. The bottles were sealed with rubber stoppers and incubated statically at 40 °C for 4 d, with regular shaking. Abiotic controls were prepared following the same procedure without addition of bacterial suspension. After bacterial degradation, liquid and gaseous samples were taken from the reaction system in triplicate for further tests.Saturate, aromatic, resin, and asphaltene analysis of crude oil
The degrading potential of bacterial formulations for crude oil was examined by quantifying the remaining total petroleum hydrocarbons (TPH) in batch cultures. TPH was extracted from 30 mL of reaction solutions with 60 mL of hexane and further fractionated into soluble and insoluble fractions using Al2O3 column chromatography.24Precipitated asphaltenes were collected by centrifugation at 4000 rpm for 5 min, and the precipitate was oven-dried at 40 °C for 24 h, cooled in a vacuum desiccator, and quantified gravimetrically.23 The soluble fraction was loaded at the top of a neutral Al2O3 column (300 mm × 10 mm ID, with a polytetrafluoroethylene stopcock at bottom) and the column was successively eluted with 80 mL of hexane, 60 mL of hexane/dichloromethane (v/v, 3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1), and 40 mL of methanol. The fractions eluted with these solvents were called saturates, aromatics, and resins. Each procedure was independently repeated three times. Bacterial degradation-associated variations (VRm%) in the mass of four crude oil fractions were described as follows:
1), and 40 mL of methanol. The fractions eluted with these solvents were called saturates, aromatics, and resins. Each procedure was independently repeated three times. Bacterial degradation-associated variations (VRm%) in the mass of four crude oil fractions were described as follows:
 | (1) |
Gas chromatography analysis
Following bacterial degradation, the crude oil was separated and diluted to 50 mg mL−1 in n-hexane. Gas chromatography (GC) analysis was performed using Thermo Finnigan Trace GC Ultra (San Francisco, CA, USA) equipped with an on-column injector, an FID detector, and a DB-Wax capillary column (30 m × 0.25 mm × 0.25 μm). The operating temperature was set to 240 °C for the FID detector and 230 °C for the injector. The column temperature was set at 40 °C for 2 min before raised to 240 °C by 6 °C min−1 and then held at 240 °C for 8 min. The sample volume was 1 μL. Nitrogen was used as a gas carrier at a constant flow rate of 1 mL min−1. The quantities of alkanes in the extracts were determined from the peak areas corresponding to these compounds on the gas chromatogram. Bacterial degradation-associated variations (VRa%) in chromatographic peak area of each n-alkane at different retention times were described as follows:
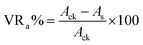 | (2) |
Surface activity determination
Surface activity was measured by the oil displacement test according to the method of Youssef et al.25 with slight modifications. Five milliliters of pre-seed inoculum with a cell density of 1010 CFU mL−1 was inoculated into 100 mL of fermentation medium and grown for 5 d at 30 °C to obtain culture broth. The oil displacement test was performed in a 25 cm diameter plastic tub containing 3000 mL of tap water. Two drops of paraffin oil (Tianli, Tianjin, China) were added to form a thin oil layer on the surface of the water. Then, cell-free culture broth obtained by centrifugation (10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 × g, 10 min, 4 °C) and one drop of it was added onto the surface of paraffin oil. The diameter of the clear zone formed on the paraffin oil surface was measured to indicate the surface activity of culture broth.
000 × g, 10 min, 4 °C) and one drop of it was added onto the surface of paraffin oil. The diameter of the clear zone formed on the paraffin oil surface was measured to indicate the surface activity of culture broth.
Emulsification index determination
Emulsifying activity was determined by adding 5 mL of paraffin oil to an equal volume of cell-free culture broth in glass tubes, followed by vortexing at high speed for 2 min and incubation at ambient temperature for 24 h. All emulsification indexes were performed in triplicate. The emulsification index (E24) was described as follows:26
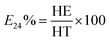 | (3) |
Crude oil removal test
A custom-designed oil removal test was performed at 40 °C under atmospheric pressure (∼0.1 MPa). Filter papers (Wohua, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China) were cut into small pieces (60 mm × 60 mm) and weighed (m) before covered with crude oil (m1). The oil-covered filter papers were transferred to 100 mL conical flasks followed by addition of 80 mL of bacterial suspensions and incubation at 40 °C for 4 d. The filter papers were then washed with water to remove surplus bacterial suspensions and dried in the air to constant weight, before weighed (m2) and photographed. Abiotic controls were prepared following the same procedure without addition of bacterial suspensions. The recyclability of bacterial suspensions was tested by repeating the test once again. Crude oil removal efficiency (RE%) was described as follows:
 | (4) |
Viscosity reduction test
To measure viscosity changes, crude oil was collected from the reaction solutions by centrifugation at 8000 rpm for 10 min. Viscosity measurement was carried out using a NDJ79 rotating viscometer (Yutong, Shanghai, China) at 40 °C under atmospheric pressure (∼0.1 MPa). Crude oil viscosity recovered from degraded samples was compared with that recovered from the control. Viscosity reduction rate (VRR%) was described as follows:
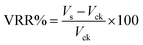 | (5) |
Gas production test
Gas samples were withdrawn from the headspace of each reaction system using a 60 mL syringe. Prior to the sampling procedure, sealed glass bottles containing the reaction solutions were shaken gently to disperse gas products. Since the pressure inside the bottle had increased due to gas production, the syringe would be filled spontaneously to a certain volume. Total gas production (Va) was recorded and CO2 was quantified by the alkali-absorption test.27 Gas production rate (GPR%) was described as follows:
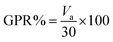 | (6) |
Gaseous components were identified by GC analysis using the 663-30 Limited gas chromatograph, equipped with an on-column injector, an FID detector, and a Porapak column (1 m × 0.05 m). Nitrogen was used as a gas carrier at the constant flow rate of 60 mL min−1. The column and injector temperatures were set to 130 °C and 160 °C, respectively. The sample volume was 5 μL.
Acid production test
For acid analysis, the reaction solutions were filtered through sterile cotton wool. The filtrate (30 mL each) was then centrifuged at 8000 rpm for 10 min and passed through a 0.22 μm Millipore filter to remove impurities. The pH of the purified filtrate was assayed with a PHS-3D pH meter (Jiapeng, Shanghai, China). Acid yield was determined by acid–base titration.The pH reduction rate (RR%), total acidity (TA), and total acid number (TAN) of purified filtrate were described using formulae (7)–(9), respectively.
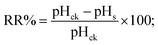 | (7) |
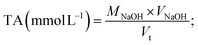 | (8) |
 | (9) |
Organic acids were identified by liquid chromatography analysis using WATERS.600, equipped with an on-column injector, a UV-vis detector (wavelength 215 nm), and a C18 column. Methanol and 0.01 mol L−1 (NH4)2HPO4 (3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 97, v/v, pH 2.8) was used as the mobile phase at a constant flow rate of 0.7 mL min−1. Oven temperature was set to 25 °C. The sample volume was 10 μL. Standard organic acid solutions were prepared as 5.0 mg mL−1 oxalate and 10 mg mL−1 formate and propionate in ultrapure water.
97, v/v, pH 2.8) was used as the mobile phase at a constant flow rate of 0.7 mL min−1. Oven temperature was set to 25 °C. The sample volume was 10 μL. Standard organic acid solutions were prepared as 5.0 mg mL−1 oxalate and 10 mg mL−1 formate and propionate in ultrapure water.
Date analysis
Data are mean ± standard deviation (n = 3). Differences between group means were identified using Duncan's multiple range test. The analysis was performed at P < 0.05 using SAS 9.2 (SAS Institute Inc, Cary, NC, USA).Funding
This study was funded by the Boqin Biological Engineering Co., Ltd., Sanyuan, Shaanxi Province, China.Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.Acknowledgements
The study was financially supported by the Boqin Biological Engineering Co., Ltd. (Sanyuan, Shaanxi Province, China). Gas and liquid chromatography data were respectively acquired at the Food Inspection Center of the College of Food Science and the Laboratory of the College of Natural Resources and Environment, Northwest A & F University (Yangling, Shaanxi Province, China). We thank Dr Laping Liu and Hong Wang for technical assistance.References
- L. R. Brown, Curr. Opin. Microbiol., 2010, 13, 1–5 CrossRef PubMed
.
- E. J. Gudiña, J. F. B. Pereira, L. R. Rodrigues, J. A. P. Coutinho and J. A. Teixeira, Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad., 2012, 68, 56–64 CrossRef
.
- R. Sen, Prog. Energy Combust. Sci., 2008, 34, 714–724 CrossRef CAS
.
- N. H. Youssef, M. S. Elshahed and M. J. Mclnerney, Adv. Appl. Microbiol., 2009, 66, 141–251 CAS
.
- N. K. Bordoloi and B. K. Konwar, Colloids Surf., B, 2008, 63, 73–82 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- H. Suthar, K. Hingurao, A. Desai and A. Nerurkar, J. Microbiol. Methods, 2008, 75, 225–230 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- I. M. Banat, A. Franzetti, I. Gandolfi, G. Bestetti, M. G. Martinotti, L. Fracchia, T. J. Smyth and R. Marchant, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2010, 87, 427–444 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- R. Rathi, M. Lavania, M. Sawale, V. Kukreti, S. Kumar and B. Lal, RSC Adv., 2015, 5, 88115–88124 RSC
.
- Y. Xu and M. Li, J. Pet. Sci. Eng., 2011, 78, 233–238 CrossRef CAS
.
- S. S. Belyaev, I. A. Borzenkov, T. N. Nazina, E. P. Rozanova, I. F. Glumov, R. R. Ibatullin and M. V. Ivanov, Microbiology, 2004, 73, 590–598 CAS
.
- F. Zhao, J. Zhang, R. J. Shi, S. Q. Han, F. Ma and Y. Zhang, RSC Adv., 2015, 5, 36044–36050 RSC
.
- Y. Al-Wahaibi, S. Joshib, S. Al-Bahry, A. Elshafie, A. Al-Bemania and B. Shibulal, Colloids Surf., B, 2014, 114, 324–333 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- A. Soudmandasli, S. S. Ayatollahi, H. Mohabatkar, M. Zareie and S. F. Shariatpanahi, J. Pet. Sci. Eng., 2007, 58, 161–167 CrossRef CAS
.
- O. Pornsunthorntawee, N. Arttaweeporn, S. Paisanjit, P. Somboonthanate, M. Abe, R. Rujiravanit and S. Chavadej, Biochem. Eng. J., 2008, 42, 172–179 CrossRef CAS
.
- S. S. M. Dastgheib, M. A. Amoozegar, E. Elahi, S. Asad and I. M. Banat, Biotechnol. Lett., 2008, 30, 263–270 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- M. Fulazzaky, D. I. Astuti and M. A. Fulazzaky, RSC Adv., 2015, 5, 3908–3916 RSC
.
- F. A. Bezza and E. M. N. Chirwa, Biochem. Eng. J., 2015, 101, 168–178 CrossRef CAS
.
- M. Souayeh, Y. Al-Wahaibi, S. Al-Bahry, A. Elshafie, A. Al-Bemani, S. Joshi, A. Al-Hashmi and M. Al-Mandhari, Energy Fuels, 2014, 28, 5606–5611 CrossRef CAS
.
- C. T. Roldán, C. G. Castorena, A. J. Reyes, P. I. Zapata and L. P. Olguín, J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol., 2013, 88, 1023–1029 CrossRef
.
- H. M. Lappin-Scott, F. Cusack and J. W. Costerton, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 1988, 54, 1373–1382 CAS
.
- H. Yang, H. Yu and Z. Y. Shen, J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2015, 42, 1139–1147 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- I. Lazar, I. G. Petrisor and T. F. Yen, Pet. Sci. Technol., 2007, 25, 1353–1366 CrossRef CAS
.
- J. H. Zhang, Q. H. Xue, H. Gao, X. Ma and P. Wang, J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol., 2015 DOI:10.1002/jctb.4650
.
- S. Mishra, J. Jyoti, R. C. Kuhad and B. Lal, Curr. Microbiol., 2001, 43, 328–335 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- N. H. Youssef, K. E. Duncan, D. P. Nagle, K. N. Savage, R. M. Knapp and M. J. Mclnerney, J. Microbiol. Methods, 2004, 56, 339–347 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- P. Das, S. Mukherjee and R. Sen, Chemosphere, 2008, 72, 1229–1234 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- P. C. Luo, Z. X. Wang, Z. Jiao and Z. B. Zhang, Chem. Ind. Times, 2004, 18, 35–40 CAS
.
- K. Sugiura, M. Ishihara, T. Shimauchi and S. Harayama, Environ. Sci. Technol., 1997, 31, 45–51 CrossRef CAS
.
- D. M. Tehrani, P. Rohanifar and S. Azami, Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2015, 12, 1253–1260 CrossRef
.
- T. S. Zhang, G. Z. Lan, L. Deng, X. F. Deng and C. Q. Zhang, Acta Pet. Sin., 2001, 22, 55–57 Search PubMed
.
- Y. H. She, F. Zhang, J. J. Xia, S. Q. Kong, Z. L. Wang, F. C. Shu and J. M. Hu, Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol., 2011, 163, 223–234 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- J. A. Felix and J. J. Cooney, J. Appl. Bacteriol., 1971, 34, 411–416 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- S. J. Joshi and A. J. Desai, Soil Sediment Contam., 2013, 22, 701–715 CrossRef CAS
.
- P. Darvishia, S. Ayatollahia, D. Mowla and A. Niazi, Colloids Surf., B, 2011, 84, 292–300 CrossRef PubMed
.
- C. G. Zheng, L. Yu, L. X. Huang, J. L. Xiu and Z. Y. Huang, J. Pet. Sci. Eng., 2012, 81, 49–56 CrossRef CAS
.
- H. Dong, Z. Z. Zhang, Y. L. He, Y. J. Luo, W. J. Xia, S. S. Sun, G. Q. Zhang, Z. Y. Zhang and D. L. Gao, RSC Adv., 2015, 5, 91869–91877 RSC
.
- C. G. Castorena, P. I. Zapata, C. T. Roldán, A. J. Reyes, C. M. Mayol, V. S. Román and L. P. Olguín, J. Pet. Sci. Eng., 2012, 81, 86–93 CrossRef
.
- D. H. Hao, J. Q. Lin, X. Song, J. Q. Lin, Y. J. Su and Y. B. Qu, Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng., 2008, 13, 61–68 CrossRef CAS
.
- A. Rabiei, M. Sharifinik, A. Niazi, A. Hashemi and S. Ayatollahi, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2013, 97, 5979–5991 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 |