Ruthenium photoredox-triggered phospholipid membrane formation†
Abstract
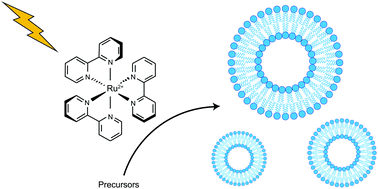
As more methodologies for generating and manipulating biomimetic cellular systems are developed, opportunities arise for combining different methods to create more complex synthetic biological constructs. This necessitates an increasing need for tools to selectively trigger individual methodologies. Here we demonstrate ruthenium tris-bipyridine mediated photoredox triggering of the copper catalyzed alkyne azide cycloaddition reaction (CuAAC), resulting in the synthesis of biomimetic phospholipids in situ, and subsequent membrane assembly. The use of a ruthenium–copper electron transport chain to trigger phospholipid assembly opens up future opportunities for spatiotemporal synthesis of membranes.
- This article is part of the themed collection: New Talent

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...