Allosteric mechanism of cyclopropylindolobenzazepine inhibitors for HCV NS5B RdRp via dynamic correlation network analysis†
Abstract
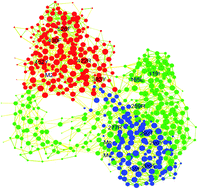
HCV RNA dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) nonstructural protein 5B (NS5B) is a major target against hepatitis C virus (HCV) for antiviral therapy. Recently discovered cyclopropylindolobenzazepine derivatives have been considered as the most potent for their ability to bind the thumb site 1 domain and allosterically inhibit HCV NS5B RdRp activity. However, the allosteric mechanism for these derivatives has not been clarified at the molecular level. In this study, fluctuation correlation networks were constructed based on all-atom molecular dynamics simulations to elucidate the allosteric mechanism. The fluctuation correlation networks between free and M2 bound NS5B are significantly different. Information can better transfer from the allosteric site to the catalytic site for bound NS5B than for free NS5B. Thus, the hypothesis of “binding induced allosteric regulation” is proposed to link the enzyme activation and inhibitor binding and then confirmed by the mutant network. Finally, one possible allosteric pathway was identified with the shortest path and evaluated by the perturbation of the network. These methods will be helpful to identify the allosteric pathway of other proteins and to design new drugs targeting the pathway.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...