Zn2+ and Cd2+ cationized serine complexes: infrared multiple photon dissociation spectroscopy and density functional theory investigations†
Abstract
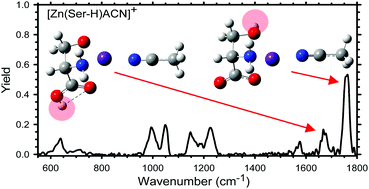
The gas-phase structures of zinc and cadmium dications bound to serine (Ser) are investigated by infrared multiple photon dissociation (IRMPD) action spectroscopy using the free electron laser FELIX, in combination with ab initio calculations. To identify the structures of the experimentally observed species, [Zn(Ser-H)CH3CN]+ and CdCl+(Ser), the measured action spectra are compared to linear absorption spectra calculated at the B3LYP/6-311+G(d,p) level for Zn2+ containing complexes and B3LYP/def2-TZVP levels for Cd2+ containing complexes. Good agreement between the observed IRMPD spectra and the predicted spectra allows identification of the isomers present. The intact amino acid interacting with cadmium chloride adopts a tridentate chelation involving the amino acid backbone amine and carbonyl groups as well as the hydroxyl group of the side-chain, [N,CO,OH]. The presence of two low-energy conformers is observed for the deprotonated serine–zinc complex, with the same tridentate coordination as for the cadmium complex but proton loss occurs at both the hydroxyl side-chain, [N,CO,O−], and the carboxylic acid of the amino acid backbone, [N,CO−,OH]. These results are profitably compared with the analogous results previously obtained for comparable complexes with cysteine.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...