Isotopically coded N-methoxy amide reagents for GC-MS profiling of carbonyl compounds via mass spectral tag generation†
Abstract
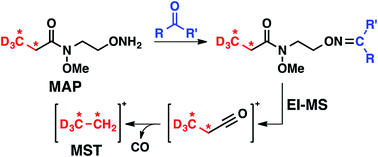
Synthesis and application of isotopically labeled N-methoxy-N-(2-aminooxyethyl)-propionate (MAP), a chemoselective carbonyl derivatization reagent, is reported. To exploit the ready measurement of fragments serving as reporter ions in the m/z 32–34 range, MAP is designed to undergo electron ionization (EI)-induced fragmentation to expel labeled ethyl carbenium ions for relative quantifications in multiplexed analyses. A study of the EI-MS fragmentation behavior of a panel of MAP–carbonyl adducts revealed that the N-methoxy amide motif of MAP is highly predisposed to undergo carbonyl alpha cleavage to produce corresponding labeled carbenium ions in the targeted m/z range. Use of the N-methoxy amide functionality decreased undesired (e.g., uninformative) mass spectral fragmentations as well as provided good resistance to cleavage by amines or base relative to ester functionality. These properties should facilitate the use of MAP in multiplexed GC-MS analyses of complex mixtures containing aldehyde and ketone analytes. A representative multiplexed experiment using MAP isotopologues illustrates this approach for quantification of a carbonyl analyte in pooled sample mixtures.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...