Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCreative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence
Isotope-filtered nD NMR spectroscopy of complex mixtures to unravel the molecular structures of phenolic compounds in tagged soil organic matter†
N. G. A.
Bell
a,
M. C.
Graham
b and
D.
Uhrín
*a
aEastCHEM School of Chemistry, University of Edinburgh, King's Buildings, David Brewster Road, Edinburgh, EH9 3FJ, UK. E-mail: dusan.uhrin@ed.ac.uk
bSchool of Geosciences, University of Edinburgh, King's Buildings, Grant Institute, James Hutton Road, Edinburgh EH9 3FE, UK
First published on 1st June 2016
Abstract
Unravelling structures of molecules contained in complex, chromatographically inseparable mixtures is a challenging task. Due to the number of overlapping resonances in NMR spectra of these mixtures, unambiguous chemical shift correlations attributable to individual molecules cannot be achieved and thus their structure determination is elusive by this technique. Placing a tag carrying an NMR active nucleus onto a subset of molecules enables (i) to eliminate signals from the non-tagged molecules, and (ii) to obtain a set of correlated chemical shifts and coupling constants belonging to a single molecular type. This approach provides an opportunity for structure determination without the need for compound separation. Focusing on the most abundant functional groups of natural organic matter molecules, the carboxyl and hydroxyl groups were converted into esters and ethers, respectively by introducing 13CH3O groups. A set of 13C-filtered nD NMR experiments was designed yielding structures/structural motives of tagged molecules. The relative sensitivity of these experiments was compared and a step-by-step guide how to use these experiments to analyse the structures of methylated phenolics is provided. The methods are illustrated using an operational fraction of soil organic matter, fulvic acid isolated from a Scottish peat bog. Analysis of 33 structures identified in this sample revealed a correlation between the position of the methoxy cross-peaks in the 1H, 13C HSQC spectra and the compound type. This information enables profiling of phenolic compounds in natural organic matter without the need to acquire a full set of experiments described here or access to high field cryoprobe NMR spectrometers.
Introduction
Natural organic matter (NOM), an assembly of thousands of organic molecules, is regarded as the most complex mixture on Earth.1 Formed by biotic and abiotic degradation of plant and animal residues,2 NOM represents an immense continuum of organic structures found in soils, natural waters and air. Accordingly, NOM plays important roles in all ecosystems.3–5 Despite its significance, the composition and the transformations of NOM on a molecular level are poorly understood. The plethora of compounds contained within NOM have resisted scientists’ use of modern analytical techniques to unravel their molecular structures. This is mostly because of our inability to isolate individual molecular constituents of NOM.6 Nevertheless, knowledge of molecular structure is crucial to the comprehension of the various roles of NOM. It will allow us to study many important processes on a molecular level e.g. the ability of phenolics7 or Sphagnum moss molecules8 to hinder peat bog degradation. To advance and fully develop the structure–function relationships of NOM molecules, we need to tackle the issue of how to determine the molecular composition of complex mixtures.Nuclear Magnetic Resonance spectroscopy (NMR) and Fourier Transform Ion Cyclotron Resonance Mass Spectrometry (FT-ICR MS) are universally acknowledged as the two best-positioned techniques to contend with the complexity of chromatographically inseparable mixtures such as NOM,9,10 but also other mixtures.11–15 However, at present, users of both techniques face significant challenges. The sheer number of compounds constituting NOM prevents the interpretation of standard multidimensional NMR spectra, making it impossible to determine the structure of individual molecules. FT-ICR MS offers incredible resolution and high mass accuracy; nevertheless, methodologies are yet to be developed that will take this technique beyond molecular formulae determination. Imaginative approaches are required that will push the boundaries of these powerful techniques to structurally characterise molecules buried in complex mixtures.
There are few examples of recent developments, such as the application of 2D HPLC-NMR16 or MSn techniques17 that provide some directions. We have proposed a combination of chemical modifications and isotope-filtered nD NMR spectroscopy as a way of simplifying NMR spectra of NOM to determine the structure of individual molecules.18,19 In this approach, NMR active isotopes contained within a molecular tag, are attached to a subset of NOM molecules. The structures of the tagged molecules are then investigated by using the tags as molecular spies that report on their immediate environment. We have proposed the use of 13CH3– tags to convert the most abundant functional groups of NOM molecules, the carboxyls and hydroxyls into esters and ethers, respectively. Focusing on the phenolic compounds we have identified 33 structures/structural fragments in an operational fraction of soil organic matter, fulvic acid isolated from a Scottish peat bog19 that was prepared according to the International Humic Substance Society (IHSS) protocols.20
Here we extend our original reports by describing a set of 13C-filtered nD NMR experiments which lead to the structure elucidation of these molecules. Even though the application of this methodology requires access to cryoprobe instruments, preferably ≥600 MHz, we suggest that its end result can be used for profiling of phenolic compounds using routine NMR instruments.
Methods
All NMR spectra were acquired in CDCl3 (550 μl) on a Bruker Avance III 800 MHz spectrometer equipped with a 5 mm TCI cryoprobe at 288 K to minimise gradient induced losses of signals caused by diffusion during long evolution intervals in the 3D INEPT-INADEQUATE-HSQC pulse sequence. The pulse sequences of proposed NMR experiments are shown in Fig. 2 and 4 and the general acquisition parameters are summarised in Table 1.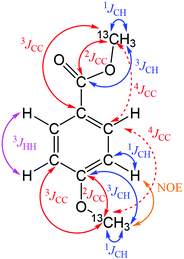 | ||
| Fig. 1 Possible polarisation transfer pathways of 13CH3O tagged phenolic molecules. Note: symmetrical pathways are depicted only once. The 4JCC indicated by dashed lines are ∼1 Hz. | ||
| Spectrum | TD/SW/AQ [number/ppm/ms] | NS | Overall time/h | Relaxation time/s | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st dimension | 2nd dimension | 3rd dimension | 4th dimension | ||||
| 2D 1H, 13C HSQC | 1024/20/128 | 6144/12/320 | — | — | 2 | 1.5 | 2 |
| 3D INEPT-INADEQUATE-HSQC | 256/75/8.5 | 128/24/13 | 3072/8/240 | — | 4 | 61 | 1.2 |
| 3D HMQC-HMBC | 320/80/10 | 96/12/20 | 3072/8/240 | — | 4 | 61 | 1.3 |
| 4D HCCH3 | 16/1.5/8.3 | 56/4/7 | 24/20/15 | 576/1.2/240 | 8 | 64 | 0.9 |
| 3D HcCH3 | 80/1.2/42 33 | 72/4/45 | 512/1.5/213 | — | 24 | 60 | 1.1 |
| 3D hCCH3 | 96/20/12 | 72/4/45 | 512/1.5/213 | — | 16 | 47 | 1.1 |
| 3D HMQC-NOESY | 64/1/40 | 224/13/42.8 | 8192/9/569 | — | 4 | 51 | 2 |
| 3D HMQC-NOESY-TOCSY | 64/1/40 | 224/13/42.8 | 8192/9/465 | — | 8 | 47 | 1.8 |
The methylation of the model mixture and the peat soil FA fraction has been described previously.18 The model mixture of nine hydroxyl benzoic acids contained the following molecules: 2-hydroxybenzoic acid, 3-hydroxybenzoic acid, 2,3-dihydroxybenzoic acid, 2,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid, 3,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid, 2,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid, 3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid, 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoic acid and 4-hydroxybenzoic acid was 13C-methylated yielding the final concentration of 1.4 mM of each compound. The NMR tubes were sealed to avoid evaporation of CDCl3 over time. The parameters used to acquire the spectra of the model mixture were similar to those used for the methylated FA sample. The latter are detailed below.
The 2D 1 H, 13C HSQC spectrum was recorded using the standard Bruker hsqcetgp sequence. The delays were optimised for a 1JCH = 145 Hz. The 1H and 13C carrier frequencies were set to 3.8 and 55 ppm. XY-32 decoupling21 was used during t2 at γB1/2π = 3571 Hz.
The 3D INEPT-INADEQUATE-HSQC spectrum was acquired using the pulse sequence published previously.18 The experiment was optimised for nJCC = 6 Hz and 1JCH = 153 Hz. The 1H and 13C carrier frequencies were set to 5.5 and 110 ppm, respectively. 2 ms composite adiabatic CHIRP 13C pulse22 was used to refocus carbon resonances, while another 500 μs CHIRP adiabatic pulse was applied to invert carbon resonances. The acquisition in t1 and t2 was delayed by half of the dwell time and the ϕ1 phase was incremented by 60° simultaneously with the t1 incrementation. The corresponding zero and first order corrections in F1 were 24°, −180°, respectively. Bi-level adiabatic decoupling was used during t3.
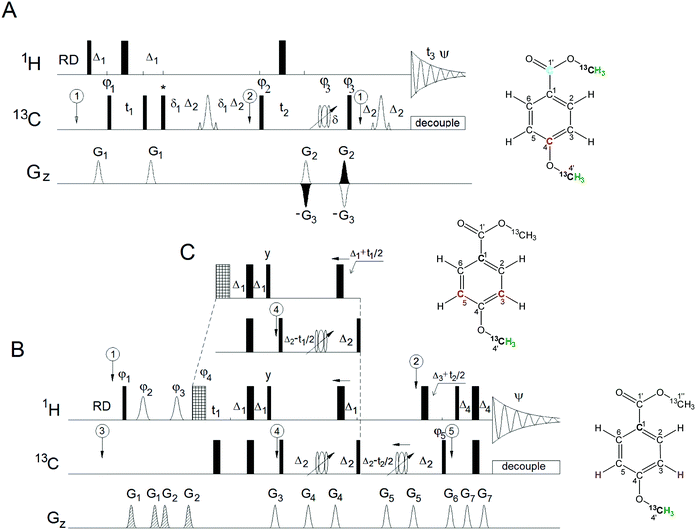
The 3D HMQC-HMBC spectrum was acquired using the pulse sequence shown in Fig. 2A. The delays were optimised for a 1JCH = 145 Hz and nJCH = 6 Hz. The 1H and 13C carrier frequencies were set to 3.8 and 115 ppm, respectively. The acquisition in t1 and t2 was delayed by half of the dwell time and the ϕ1 phase was incremented by −50° simultaneously with t1 incrementation. The corresponding zero and first order corrections in F1 were 153°, −180°, respectively. A 2 ms composite adiabatic CHIRP 13C pulse was utilised for refocusing of carbon resonances while a 150 μs r-SNOB 180° pulse was used to refocus the 1JCH3 evolution during the HMBC step. XY-32 decoupling was used during t3 at γB1/2π = 3571 Hz.
The 4D HCCH 3 spectrum was acquired using the pulse sequence published previously.19 The delays were optimised for a 1JCHarom = 155 Hz, 3JCC = 6 Hz and 1JCH3 = 145 Hz. To reduce off-resonance effects the carrier frequencies were changed at specific places. The 13C frequency offsets were changed from 56 to 110 to 96 then back to 56 ppm, while the 1H offsets were changed from 7.5 to 5.5 and finally to 3.8 ppm during the pulse sequence. The acquisition in t1, t2 and t3 was delayed by half of the dwell time and the ϕ5 phase was incremented by 135°, while the ϕ6 phase was incremented by −20° simultaneously with t2 and t1 incrementation, respectively. This required the zero and first order phase corrections to be set to 90°, −180° in F1, 188°, −180° in F2 and 154°, −180° in F3. 2 ms composite adiabatic CHIRP 13C pulses were utilised for refocusing carbon resonances. A 1 ms trim pulse was applied after the Double Pulsed Field Gradient Spin Echo (DPFGSE) with full power, while 1 ms r-SNOB 180° pulses were used for the DPFGSE. XY-32 decoupling was used during t4 at γB1/2π = 3571 Hz.
The 3D HcCH 3 spectrum was acquired using the pulse sequence shown in Fig. 2B. The acquisition in t1 and t2 was delayed by half of the dwell time and phases ϕ1 to ϕ4 were incremented by −20° simultaneously with t1 incrementation. This required setting the zero and first order phase corrections to 83°, −180° in F1 and 90°, −180° in F2. Other parameters were the same as for the 4D HCCH3 experiment.
The 3D hCCH 3 spectrum was acquired using the pulse sequence shown in Fig. 2C. The acquisition in t1 and t2 was delayed by half of the dwell time and phase ϕ5 was incremented by +135°, while ϕ6 was incremented by −90° simultaneously with t1 and t2 incrementation, respectively. This required to set the zero and first order phase corrections to 28°, −180° in F1 and 129°, −180° in F2. Other parameters were the same as for the 4D HCCH3 experiment.
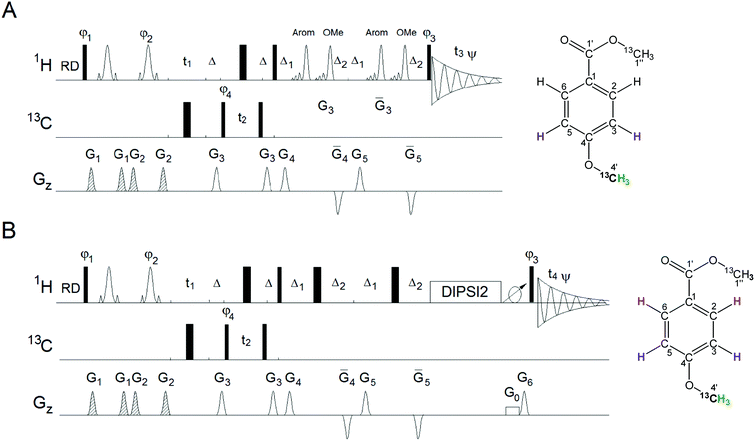
The 3D HMQC-NOESY spectrum was acquired using the pulse sequence shown in Fig. 4A. The NOESY mixing time was set to 600 ms. The carrier frequencies in 1H and 13C dimensions were 3.9 and 56.6 ppm, respectively. The acquisition in t1 and t2 was delayed by half of the dwell time, with the corresponding phases set to 90° in the DPFGSE. Two 2.8 ms 180° IBURP2 pulses were applied at 3.9 and 7.4 ppm two times at specified intervals during the NOESY mixing interval. The second pulse was created by time inverting the IBURP2 profile and phase shifting it to invert the aromatic protons.
The 3D HMQC-NOESY-TOCSY spectrum was acquired using the pulse sequence shown in Fig. 4B. The NOESY and TOCSY mixing times were 600 and 80 ms, respectively. Two hard 180° pulses were used during the mixing time.23 In order to remove zero quantum coherences24 a 20 ms adiabatic CHIRP pulse was applied simultaneously with 4% gradient after the DIPSI2 spin-lock using γB1/2π = 10 kHz. Other parameters were the same as for the 3D HMQC-NOESY experiment.
Pulse sequences of the proposed NMR experiments are given in the ESI.†
Results and discussion
Description of 13CH3O-filtered nD NMR experiments
Isotope tagging places an NMR active nucleus onto the target molecules by modifying their functional groups. Such a nucleus serves a dual purpose. It eliminates NMR signals from non-tagged molecules in the NMR spectra and reports on the chemical shifts of nearby nuclei. In this work the 13C tagging was achieved using 13CH3I as described previously.18,19 Methylation by 13CH3I is non-selective and modifies both phenols and aliphatic hydroxyl groups. In addition, it also converts aromatic and aliphatic carboxyl groups into methyl esters. In order to extract the chemical shifts of the tagged molecules nuclei, several nD 13CH3O-filtered NMR experiments are required. These combine multiple polarisation transfer steps, initiating with passage through the nuclei of the 13CH3O group enabled by numerous J couplings of this tag (Fig. 1). For phenolic compounds, the relevant coupling constants (Table 2) were measured on a mixture of nine model compounds.18 In the following, 13C-filtered 3D experiments utilising these tags to report on their environment are described. Their relative sensitivity and individual merits are discussed. An example is given to illustrate how best to analyse the obtained spectra to achieve molecular level characterisation of phenolic compounds.| Coupling type | Coupling constant range (Hz) |
|---|---|
| a The interacting nuclei are highlighted in bold. | |
| 1 J CH3 | 142–145 |
| 1 J CHar | ∼150 |
| 3 J COCH3 | 3.3–4.1 |
| 2 J COCH3 | 2.3–3.5 |
| 3 J CCOCH3 | 3–5 |
| 3 J HH | 7–9 |
3D INEPT-INADEQUATE-HSQC
This experiment, applied to a mixture of nine 13CH3O– tagged model compounds, has been described previously,18 therefore only a brief outline is presented here. INADEQUATE25 is the ultimate NMR experiment for the structure determination of organic molecules, as it allows their carbon skeletons to be traced. However, its reliance on the presence of two 13C nuclei in the same molecule lowers the sensitivity and consequently the application scope of this experiment. However, this is not an issue here, as only the nJ(13C, 13C) couplings involving 100% enriched 13CH3O– groups are utilised. To boost the sensitivity of the experiment further proton detection along the lines of the 2D INEPT-INADEQUATE experiment was employed.26 This experiment provides double-quantum (DQ) 13C frequencies of coupled carbon nuclei and the 1H chemical shifts of protons attached to carbons forming the DQ coherences. The lost 13C chemical shift information is recovered by incorporating constant-time single quantum (SQ) chemical shift labelling27,28 into one of the long evolution intervals of the experiment. The resulting 3D INEPT-INADEQUATE-HSQC is a very powerful NMR experiment that provides numerous chemical shifts of tagged molecules.18 Specifically, carbon chemical shifts of ipso, ortho and occasionally meta carbons relative to the methoxy groups, proton chemical shifts of the ortho protons and the proton and carbon chemical shifts of the methoxy groups. A partial 3D spectrum of 13C-methylated peat soil fulvic acid obtained from this experiment is shown in Fig. 3, together with the spectra of the rest of the experiments discussed below.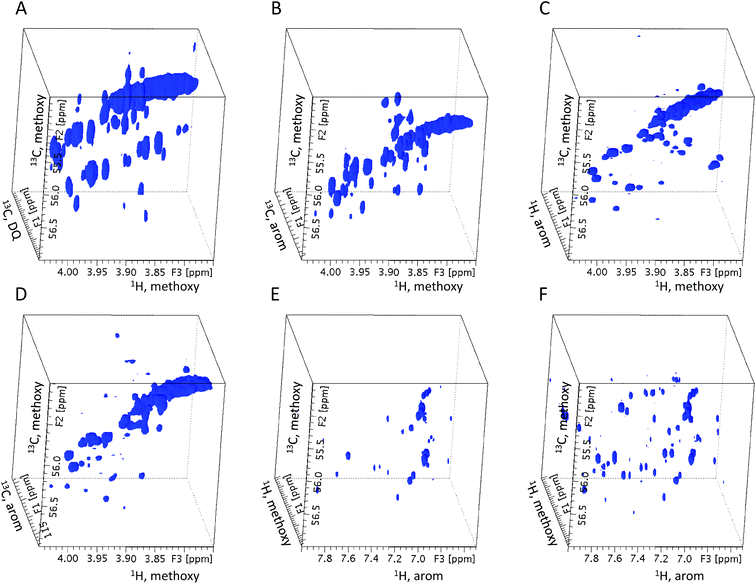 | ||
| Fig. 3 Partial 3D spectra of 13C-methylated peat soil fulvic acid. (A) 3D INEPT-INADEQUATE-HSQC (B) 3D HMQC-HMBC (C) 3D HcCH3 (D) 3D hCCH3 (E) 3D HMQC-NOESY (F) 3D HMQC-NOESY-TOCSY. | ||
3D HMQC-HMBC
The 3D HMQC-HMBC experiment (Fig. 2A) correlates the chemical shifts of the quaternary carbon carrying a 13CH3O– group with the chemical shifts of the methoxy group nuclei. The pulse sequence of the 3D HMQC-HMBC starts with a HMQC part, where the 13C chemical shifts of the methoxy carbons are labelled (t1), followed by the creation of an anti-phase methyl proton magnetisation with respect to the quaternary ipso carbons. Once this is converted into MQ coherences, the chemical shifts of the quaternary carbons are labelled in the HMBC part of the sequence, followed by a back conversion to proton magnetisation prior to the detection under 13C decoupling. The evolution of 1JCH3 couplings of fully labelled methoxy groups during the long evolution intervals of the HMBC part of the pulse sequence need to be suppressed. This is achieved by (i) setting the HMQC Δ1 interval to the average 1/2 1JCH3 value followed by conversion by a 90° 13C pulse of any imperfectly refocused signals at the end of the HMQC sequence into MQ coherences; (ii) selective inversion of methoxy carbons mid-way through the defocusing and refocusing periods of the HMBC part of the pulse sequence. This is a far more effective way to eliminate the overall 1JCH3 evolution than setting the long-range evolution intervals to an even multiple of 1/2 1JCH3 using an average value of 1JCH3.3D/4D HCCH3
The HCCH3 experiments provide chemical shifts of the CH moieties ortho to a methoxy group as well as the proton and carbon chemical shifts of this methoxy group. Although the 3D INEPT-INADEQUATE-HSQC experiment18 also provides in principle the chemical shifts of all HCCH3 nuclei in a single experiment, the S/N of aromatic protons in the INADEQUATE spectra is noticeably lower than that of the methoxy protons. This is because the three protons of the methoxy group show as singlets in NMR spectra, while in general, aromatic protons are presented as multiplets in the INADEQUATE spectra. The HCCH3 experiments record the aromatic proton chemical shifts in the indirectly detected dimension, thus alleviating this problem.Chemical shift labelling of all nuclei along the HCCH3 polarisation transfer pathway naturally leads to a 4D experiment. The 4D HCCH3 experiment provides an excellent insight into the substitution patterns of phenolic molecules by separating signals into four dimensions, as demonstrated previously.19 A limiting factor, common to all 4D NMR experiments, is that adding a 4th dimension reduces the sensitivity and compromises the achievable resolution relative to 3D experiments. This issue is addressed here by two complementary 3D experiments, 3D HcCH3 and 3D hCCH3, which in addition to the nuclei of the methoxy group, only label chemical shifts of either the aromatic protons or carbons.
The 3D HCCH3 experiments (Fig. 2B and C) start with the excitation of aromatic protons and end with the detection of methyl protons. The initial selection of the aromatic protons is achieved by a DPFGSE29 containing r-SNOB pulses,30 which were chosen due to their near ‘top-hat’ profile. The DPFGSE eliminates phase errors across the inverted frequency range and is therefore preferable to a shorter SPFGSE sequence. Both 3D HCCH3 experiments follow the magnetisation pathway of the 4D HCCH3, but differ in whether the chemical shits of the aromatic protons or carbons are labelled. In the HcCH3 experiment, the chemical shifts of the aromatic protons are labelled during the t1 period before an INEPT transfer to the aromatic carbons, while in the hCCH3 experiment the chemical shifts of the aromatic carbons are labelled after the transfer. Once the magnetisation is on the aromatic carbons, the spin system evolves to create an antiphase magnetisation with regard to the methoxy carbon while refocusing the 1JCHarom couplings. The magnetisation is then passed to the methoxy carbons for chemical shift labelling during t2, before transfer to the methyl protons for detection during t3. The carbon decoupling over a narrow range of methyl carbon resonances with reduced power allows longer acquisition and thus very good signal resolution.
3D HMQC-NOESY
The 3D HMQC-NOESY experiment is an alternative for obtaining the chemical shifts of protons ortho to the methoxy group. Unlike in the experiments described above, here the magnetisation does not pass through the natural abundance 13C atoms thus avoiding the inevitable sensitivity loss of heterocorrelated experiments. The observed efficiency of the NOE transfer between methoxy and aromatic ring protons investigated by a 1D NOESY experiments on the mixture of nine methylated compounds was around 4% (data not shown). This exceeds the natural abundance of 13C (1%), thus providing higher sensitivity, albeit with reduced information content by not including the 13C chemical shifts. Nevertheless, the 3D HMQC-NOESY experiment proved very useful, in part because it also yields the proton–proton couplings, thus providing additional structural information.The 3D HMQC-NOESY experiment (Fig. 4A) starts with a DPFGSE, selecting methoxy protons, followed by chemical shift labelling of methoxy carbons during the t2 period of the refocused HMQC pulse sequence. Chemical shifts of the methoxy protons are labelled during the t1 period and their magnetisation is then positioned along the z-axis, by the action of a 90° 1H pulse, for NOE transfer. An efficient NOE transfer for small molecules requires long NOE build-up times (>0.5 s), during which considerable auto relaxation occurs. This leads to the appearance of axial peaks at the zero F1 frequency and an overall increase in the t1 noise. These effects can be reduced by inverting resonances during the NOE mixing time.29 In addition, using selective rather than nonselective pulses to achieve this, the NOE transfer is restricted between the groups of inverted protons.31 When only aromatic and methoxy protons are inverted, leakage of magnetisation from methoxy to other aliphatic protons is therefore eliminated. As shown by Stott et al. placing one 180° pulse in the middle of the mixing time interval is less efficient, compared to two pulses spaced appropriately. It is best to use two 180° pulses, one at ∼0.25τmix and the other at ∼0.75τmix to get efficient artefact suppression. Band selective IBURP2 pulses32 were used here because of their ‘top hat’ inversion profile. In order to avoid the so-called ‘close encounter’ effects between soft pulses when two neighbouring regions are inverted simulteneously,33 the pulses inverting the methoxy and aromatic resonances were applied consecutively. There is no need for carbon decoupling in this pulse sequence, which allowed longer acquisition times to be used, providing accurate readouts of the proton–proton coupling constants of aromatic protons.
3D HMQC-NOESY-TOCSY
It is straightforward to extent the 3D HMQC-NOESY pulse sequence to construct a 3D HMQC-NOESY-TOCSY experiment (Fig. 4B). This involves appending the NOESY pulse sequence with a DIPSI-2 spin-lock34 containing a ZQ interference removal element24 applied after the TOCSY spinlock. In this experiment the band selective inversion pulses applied during the NOESY mixing time were replaced by non-selective pulses, as the molecules in the studied sample have no prospect of NOE transfer from methoxy to other aliphatic protons. This modification can also be applied to the 3D HMQC-NOESY experiment.Relative sensitivity of the isotope-filtered nD experiments
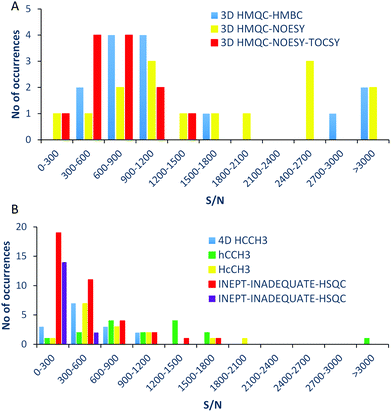
The discussed pulse sequences produce high quality 3D spectra, nevertheless, as there is a partial redundancy in the obtained chemical shifts, it is useful to compare their performance. The S/N ratios achievable by individual experiments were therefore investigated by acquiring 3D/4D NMR spectra of a model mixture of nine methylated aromatic compounds. As much as possible, similar experimental conditions were used for this comparison. In particular, the digital resolution in the indirectly detected dimensions was kept the same. In order to achieve this, while at the same time accommodating different spectral widths required by individual experiments, different overall acquisitions times had to be used. These differences were eliminated by scaling the measured S/N ratios relative to the S/N of a 3D INEPT-INADEQUATE-HSQC spectrum obtained in a 14 hour long experiment.18 As all experiments provide 1H, 13C correlations of the methoxy groups, 1D traces were extracted from the HSQC/HMQC planes at individual methoxy carbon chemical shifts. The S/N in these traces was measured for methoxy protons except for the 3D HMQC-NOESY and 3D HMQC-NOESY-TOCSY, where the S/N was determined for aromatic protons. The NOESY peaks were not included when evaluating the TOCSY spectra. The S/N ratio of the 3D INEPT-INADEQUATE-HSQC spectrum was measured in both aromatic and methoxy regions. The S/N of the 4D HCCH3 spectrum was obtained by extracting 3D cubes at individual methoxy 13C chemical shifts, followed by the extraction of 1D slices from the 2D HSQC planes, as done for the 3D experiments. The obtained data are presented in two graphs (Fig. 5A and B) for clarity in the form of bar charts, where the count represents the number of cross-peaks with a particular S/N ratio within a 0–3000 range, increasing in steps of 300. From the comparison of the S/N ratios obtained, it is clear that the discussed experiments are not vastly different in terms of their sensitivity. As expected, the 3D HCCH3 experiments show better S/N compared to the 4D HCCH3 experiment. The INEPT-INADEQUATE-HSQC has the lowest sensitivity, which again is to be expected due to the inclusion of DQ coherences in the polarisation transfer pathway of this experiment. The 3D HMQC-NOESY experiment is the most sensitive, followed by the 3D HMQC-HMBC experiment.Practical guide to the interpretation of 13CH3O-filtered nD NMR spectra of tagged complex mixtures
Only the 3D INEPT-INADEQUATE-HSQC and 3D HMQC-HMBC spectra provide chemical shifts of quaternary carbons. The 3D INEPT-INADEQUATE-HSQC spectra yield the chemical shifts of CH atoms ortho to the methoxy groups, as do the HCCH3-type experiments. The 3D INEPT-INADEQUATE-HSQC could thus be regarded as the most important experiment for the analysis of phenolic compounds, as it identifies all accessible carbon chemical shifts, including the ortho carbons (regardless if protonated or not). However, as can be seen from the S/N comparison presented in Fig. 5, the sensitivity of the 3D HMQC-HMBC and 3D HCCH3 experiments is higher than that of the 3D INEPT-INADEQUATE-HSQC. The 3D HMQC-NOESY-TOCSY yields chemical shifts of additional aromatic protons and therefore provides valuable information extending the characterised structures.While the interpretation of 13C-filtered nD spectra of 13CH3O-tagged NOM can be approached in several different ways, a particular procedure that efficiently pieces together molecular structures of phenolic molecules is summarised next. This is illustrated on the structure determination of a compound carrying a methoxy group resonating at δ13C/1H of 55.41/3.87 ppm. The process can be divided into the following six steps:
1. Identify methoxy cross-peaks in the 2D 1H, 13C HSQC spectrum.
2. Using the 3D HMQC-HMBC spectrum, determine the chemical shifts of ipso carbons associated with individual methoxy cross-peaks of the 1H, 13C HSQC spectrum.
3. Using the HCCH3 spectra, identify chemical shifts of protonated aromatic CH moieties ortho to the methoxy groups (if there is no corresponding cross-peaks in 4D or 3D HCCH3 spectra, then the methoxy group is either surrounded by two quaternary carbons or it is not attached to an aromatic molecule).
4. Verify the assignments obtained in points 2 and 3 by inspecting the 3D INEPT-INADEQUATE-HSQC spectrum. Identify any additional cross-peaks, especially belonging to the quaternary carbons. Extra (weak) cross-peaks may belong to carbons meta to the methoxy group.
5. Extend the 1H spin systems by inspecting the 3D HMQC-NOESY and HMQC-NOESY-TOCSY spectra.
6. Examine cross-peaks in the 3D HMQC-HMBC and 3D INEPT-INADEQUATE-HSQC spectra associated with the methoxy ester groups. Cross reference with the weak cross-peaks associated with phenolic methoxy groups.
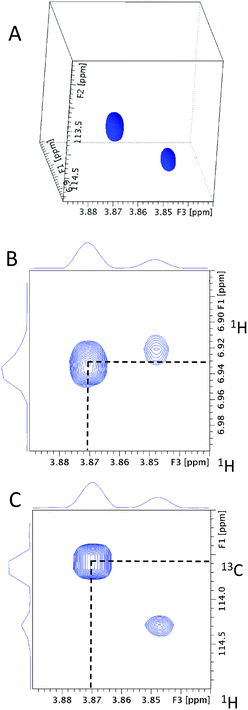
As a starting point, the 55.41 ppm F1F3 2D plane of the 3D HMQC-HMBC spectrum is inspected. The chemical shift of the ipso carbon at 163.32 ppm (Fig. 6) confirms that this methoxy group is joined to an aromatic ring.
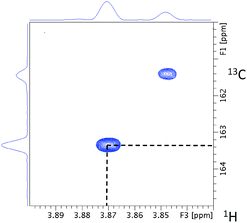 | ||
| Fig. 6 The 55.41 ppm F1F3 2D plane extracted from the 3D HMQC-HMBC spectrum of 13C methylated FA. The cross-peak with the 3.87 ppm methoxy proton chemical shift is highlighted. | ||
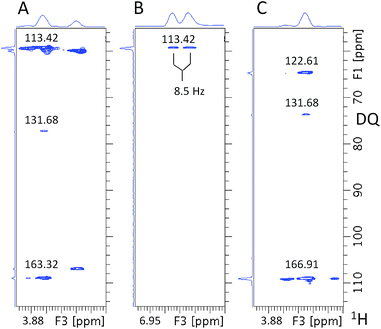
Next, any ortho CH moieties are identified by inspecting the 4D/3D HCCH3 spectra. A 3D cube extracted from the 4D HCCH3 spectrum through the methoxy carbon at 55.41 ppm is shown in Fig. 7A. The 55.41 ppm F1F3 2D planes from the 3D hCCH3 and HcCH3 spectra (Fig. 7B and C) contain two cross-peaks; the one at the correct methoxy proton chemical shift of 3.87 ppm is indicated by the dotted lines. This analysis associates the HC atoms at 6.93/113.42 ppm with the investigated methoxy group. As only one CH pair was identified, the molecule is either symmetrical around the methoxy group, or the other ortho position contains a quaternary carbon.
Fig. 8 shows the 55.41 ppm F1F3 2D plane extracted from the 3D INEPT-INADEQUATE-HSQC spectrum. Its methoxy region (Fig. 8A) contains three cross-peaks at the methoxy proton chemical shift of 3.87 ppm. The two most intense signals with the 13C chemical shifts of 113.42 and 163.32 ppm have already been identified by previous experiments as belonging to ortho and ipso carbons, respectively. An additional cross-peak at 131.68 ppm is much weaker than that at 113.42 ppm and therefore does not represent the second ortho proton. This analysis confirms that the corresponding fragment is likely symmetrical around the methoxy group. The aromatic region of the plane (Fig. 8B) shows only one aromatic proton resonating at 6.93 ppm, reflecting the symmetry of the molecule. Its signal appears as a doublet (J = 8.5 Hz), indicating that the meta carbons relative to the methoxy group are protonated.
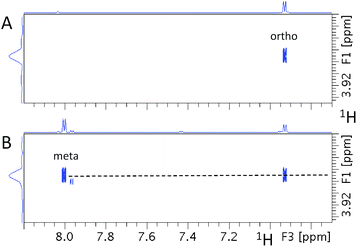
Fig. 9 shows the 55.41 ppm F1F3 2D planes extracted from the 3D HMQC-NOESY and 3D HMQC-NOESY-TOCSY spectra. The signal at 6.93 ppm (J = 8.5 Hz) belongs to protons ortho to the methoxy group. The only other signal identified in the 3D HMQC-NOESY-TOCSY spectrum is a doublet at 7.99 ppm, confirming that this molecule is symmetrical.
In summary, information gathered thus far consistently indicates that the analysed molecule is a para di-substituted benzene with a methoxy group at one end of the molecule.
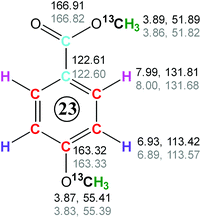
When the obtained chemical shifts of the investigated fragment were compared with the database chemical shifts of the methoxy benzene35,36 it became clear that the substituent para to the methoxy group has a large ortho deshielding effect, as indicated by the increased proton chemical shift (7.99 ppm). This is typical for an electron-withdrawing group such as a carboxylic acid or an ester. To examine if the para position carries a methyl ester group, the carboxyl region of the 3D HMQC-HMBC was inspected (data not shown). Considering the database chemical shifts35 of the ester group of methyl p-methoxy benzoate (166.82, 51.82 and 3.86 ppm), the 51.89 ppm F1F3 2D plane of the 3D INEPT-INADEQUATE-HSQC spectrum was inspected. It showed three cross-peaks at SQ 13C chemical shifts of 166.91, 122.61 and 131.81 ppm, respectively (Fig. 8C). The first two intense cross-peaks belong to the carbonyl of the ester group and the ipso quaternary carbon of the aromatic ring, respectively. The remaining weak correlation at 131.84 ppm involves the aromatic carbons ortho to the methyl ester group. This correlation was also identified as a weak cross-peak in the methoxy ether region of the 3D INEPT-INADEQUATE-HSQC spectrum (Fig. 8A), which indicates that it belongs to the same molecule.
A comparison of the database and the experimental chemical shifts (Fig. 10) showed an excellent agreement, indicating that the inspected molecule is methyl p-methoxybenzoate. It should be noted that the 4JCH3,C carbon–carbon couplings are small and correlations such as involving 13C at 131.81 ppm mediated by these couplings will only be observed for the most abundant compounds. Nevertheless, even in the absence of this information, the structure of this compound would have been identified by analysing the chemical shifts associated with the methoxy group.
Analogous analysis starting with the methoxy cross-peaks present in the 1H, 13C HSQC spectrum of the methylated FA sample (Fig. 11) identified 33 structures/structural fragments as reported previously19 (Fig. 1S of the ESI†). This spectrum shows a typical diagonal trend between the proton and carbon chemical shifts. Analysis of the identified compounds/structural fragments revealed that the cross-peaks can be divided into four groups labelled (a) to (d) as shown in Fig. 11. Region (a) contains resonances of methoxy groups of p-disubstituted benzene rings, while region (b) contains methoxy groups of 3,4-disubstituted rings, with an exception of cross-peak 25 that belongs to the one of the two 3,5 methoxy groups of a 3,5-disubstituted molecule 25/28. Region (c) is the most heterogeneous in terms of the structures of its molecules. Cross-peak 28 belongs to the other methoxy group of molecule 25/28, while cross-peaks 14 and 19 belong to compounds containing three methoxy groups. Molecule 19 only contains one 13C-labelled and two unlabelled methoxy groups, while in molecule 14 all OH groups at positions 3, 4, 5 were 13C-methylated (the C4 OMe group is not shown in Fig. 11, as its carbon resonates at 60.89 ppm). The remaining molecules of this group had only one methoxy group located next to an unsubstituted CH site on otherwise highly substituted aromatic rings containing 2 to 3 additional substituents. Region (d) contains signals of methoxy groups located next to an unsubstituted CH site on otherwise highly substituted rings containing 3 to 4 additional non-oxygen containing substituents, i.e. similar to some molecules of the previous group, albeit with a different character of substituents causing further deshielding of methoxy resonances.
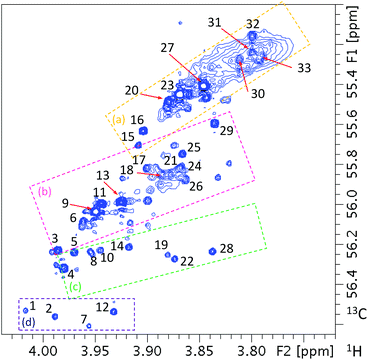 | ||
| Fig. 11 Methoxy region of 2D 1H, 13C HSQC spectrum of 13C methylated FA. The cross-peak labels correspond to the compounds given in Fig. 1S of the ESI.† The dashed rectangles delineate regions discussed in the text. | ||
This grouping of cross-peaks enables a quick assessment of compound types present in 13C methylated mixtures without the need for a full analysis along the lines presented here. Based only on a 2D 1H, 13C HSQC spectra of 13C methylated mixtures, which can be acquired on a standard NMR spectrometer equipped with a room temperature probe, this classification will improve when more mixtures are fully characterised.
Conclusions
A series of isotope-filtered nD NMR experiments designed for the structure elucidation of 13CH3O-labelled mixture was presented. Their application to a peat FA sample illustrates how structures of aromatic compounds contained in a complex mixture can be obtained. Analysis of these experiments indicates that in an ideal case only two experiments are required for full molecular characterisation, 3D INEPT-INADEQUATE-HSQC and the HMQC-NOESY-TOCSY. However, for less abundant compounds yielding weaker signals, it is recommended to acquire a whole suite of experiments to overcome the sensitivity and potential overlap issues. It can be envisaged that similar experiments can be designed for different compound classes and/or different tags. Although illustrated here on a NOM sample, this approach is not limited to studies of the mixtures found in the environment and can applied other complex mixtures, such as food and beverages, bio fluids, plant extracts, or lignin degradation products.Acknowledgements
N. G. A. Bell would like to thank NERC and the University of Edinburgh Principal's Scholarship for funding. This work was supported by the NERC grant NE/L00044X/1 to M. C. Graham and D. Uhrin. The authors would like to thank Juraj Bella and Dr Lorna Murray for maintenance of the 800 MHz NMR spectrometer, Dr Murray for methylation of the model mixture, Mr Adam Michalchuk for preparation of the FA sample and Mr John Blackburn for carrying out methylation of this sample.Notes and references
- S. Derenne and C. Largeau, Soil Sci., 2001, 166, 833–847 CrossRef CAS.
- R. L. Wershaw, U.S. Geological Survey, 2004 Search PubMed.
- M. J. Simpson and A. J. Simpson, J. Chem. Ecol., 2012, 38, 768–784 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Noziere, M. Kaberer, M. Claeys, J. Allan, B. D'Anna, S. Decesari, E. Finessi, M. Glasius, I. Grgic, J. F. Hamilton, T. Hoffmann, Y. Iinuma, M. Jaoui, A. Kahno, C. J. Kampf, I. Kourtchev, W. Maenhaut, N. Marsden, S. Saarikoski, J. Schnelle-Kreis, J. D. Surratt, S. Szidat, R. Szmigielski and A. Wisthaler, Chem. Rev., 2015, 115, 3919–3983 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Steinberg, Ecology of Humic Substances in Freshwaters: Determinants from Geochemistry to Ecological Niches, Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2013 Search PubMed.
- N. Hertkorn, C. Ruecker, M. Meringer, R. Gugisch, M. Frommberger, E. M. Perdue, M. Witt and P. Schmitt-Kopplin, Anal. Bioanal. Chem., 2007, 389, 1311–1327 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Freeman, N. Ostle and H. Kang, Nature, 2001, 409, 149–149 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Hajek, S. Ballance, J. Limpens, M. Zijlstra and J. T. A. Verhoeven, Biogeochemistry, 2011, 103, 45–57 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Hertkorn, R. Benner, M. Frommberger, P. Schmitt-Kopplin, M. Witt, K. Kaiser, A. Kettrup and J. I. Hedges, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 2006, 70, 2990–3010 CrossRef CAS.
- A. J. Simpson, D. J. McNally and M. J. Simpson, Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc., 2011, 58, 97–175 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. S. McKenzie, J. A. Donarski, J. C. Wilson and A. J. Charlton, Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc., 2011, 59, 336–359 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Jeannerat and J. Furrer, Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screening, 2012, 15, 15–35 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Novoa-Carballal, E. Fernandez-Megia, C. Jimenez and R. Riguera, Nat. Prod. Rep., 2011, 28, 78–98 RSC.
- J.-L. Wolfender, G. Marti, A. Thomas and S. Bertrand, J. Chromatogr., A, 2015, 1382, 136–164 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. R. Forseth and F. C. Schroeder, Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol., 2011, 15, 38–47 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. C. Woods, M. J. Simpson, P. J. Koerner, A. Napoli and A. J. Simpson, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2011, 45, 3880–3886 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Witt, J. Fuchser and B. P. Koch, Anal. Chem., 2009, 81, 2688–2694 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. G. A. Bell, L. Murray, M. C. Graham and D. Uhrin, Chem. Commun., 2014, 50, 1694–1697 RSC.
- N. G. A. Bell, A. A. L. Michalchuk, J. W. T. Blackburn, M. C. Graham and D. Uhrin, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2015, 54, 8382–8385 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. M. Thurman and R. L. Malcolm, Environ. Sci. Technol., 1981, 15, 463–466 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. J. Kotyk, J. Magn. Reson., 1991, 95, 632–635 CAS.
- L. Emsley and G. Bodenhausen, J. Magn. Reson., 1992, 97, 135–148 CAS.
- K. Stott, J. Keeler, Q. N. Van and A. J. Shaka, J. Magn. Reson., 1997, 125, 302–324 CrossRef CAS.
- M. J. Thrippleton and J. Keeler, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2003, 42, 3938–3941 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Bax, R. Freeman and S. P. Kempsell, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1980, 102, 4849–4851 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Weigelt and G. Otting, J. Magn. Reson., Ser. A, 1995, 113, 128–130 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Chung, J. R. Tolman, K. P. Howard and J. H. Prestegard, J. Magn. Reson., Ser. B, 1993, 102, 137–147 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Saito and R. L. Rinaldi, J. Magn. Reson., Ser. A, 1996, 118, 136–139 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Stott, J. Stonehouse, J. Keeler, T. L. Hwang and A. J. Shaka, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1995, 117, 4199–4200 CrossRef CAS.
- E. Kupce, J. Boyd and I. D. Campbell, J. Magn. Reson., Ser. B, 1995, 106, 300–303 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Zwahlen, S. J. F. Vincent, L. Dibari, M. H. Levitt and G. Bodenhausen, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1994, 116, 362–368 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Geen and R. Freeman, J. Magn. Reson., 1991, 93, 93–141 Search PubMed.
- E. Kupce and R. Freeman, J. Magn. Reson., Ser. A, 1995, 112, 261–264 CrossRef CAS.
- S. P. Rucker and A. J. Shaka, Mol. Phys., 1989, 68, 509–517 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Ralph, S. Ralph and L. Landucci, United States Forest Product Laboratory, https://www.glbrc.org/databases_and_software/nmrdatabase/NMR_DataBase_2009_Complete.pdf, 2004.
- Spectral Database for Organic Compounds, SDBSWeb, National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology, http://sdbs.db.aist.go.jp, 2015 Search PubMed.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: 10.1039/c6an00999a |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 |