A mechanical pencil lead-supported carbon nanotube/Au nanodendrite structure as an electrochemical sensor for As(iii) detection†
Abstract
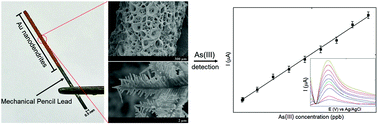
A mechanical pencil lead (MPL), an easily obtainable carbon-based material with a consistent size, was used as a frame to construct an MPL-supported carbon nanotube/Au nanodendrite (MPL-CNT/AuND) sensor through simple electrodeposition of Au onto the MPL in the presence of CNTs. A nanodendrite structure was adopted to ensure large numbers of active electrochemical sites because of its hierarchical structure with well-aligned terraces; the CNTs were used to firmly adhere the fabricated Au nanodendrites to the MPL surface to ensure ruggedness. The MPL-CNT/AuND structure was used to measure As3+ samples in a concentration range from 0.5 to 80 ppb using anodic stripping voltammetry (ASV). The variation in peak intensities was linear (R2: 0.997), and the limit of detection (LOD) was 0.4 ppb. The average relative standard deviation (RSD) of the peak intensities from the voltammograms of each sample collected using three separately prepared MPL-CNT/AuNDs was 8.7%, thereby demonstrating good sensor-to-sensor reproducibility. Furthermore, when three As3+ samples prepared in tap water were measured, the accuracy was maintained without noticeable degradation and the response was steady up to 50-cycle measurements.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Carbon and graphene in analytical science

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...