Synthesis of azo carbonate monomers and biocompatibility study of poly(azo-carbonate-urethane)s†
Abstract
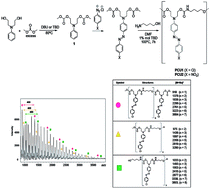
The present work describes the synthesis of azo carbonate monomers by a clean carbonylation synthetic route using di-methylcarbonate. The kinetics study showed a conversion of ∼98% to bis-carbonates after only six minutes of reaction using triazabicyclo[4.4.0]dec-5-ene (TBD) as the catalyst. The preparation of azo-carbonates by means of coupling aryldiazonium salts with bis-carbonate was performed. The reactivity of azo-carbonate monomers was tested in the polycondensation reaction with an aminoalcohol using TBD as a catalyst for the formation of non-isocyanate poly(azo-carbonate-urethane)s PCU 1 and PCU 2. The copolymers’ structures were confirmed by FT-IR, NMR and MALDI experiments, which allow us to determine the different terminal groups of the polymer chains formed. The molecular weights and the molecular weight distribution of PCU 1 and PCU 2 were determined by size-exclusion chromatography (SEC) experiments and thermal stabilities were also studied by TG analysis. The biocompatible properties of monomers 4 and 6 and polymers PCU 1 and PCU 2 were investigated by liver, kidney and colon histological analyses.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...