Proteomic responses to gold(iii)-toxicity in the bacterium Cupriavidus metallidurans CH34†
Abstract
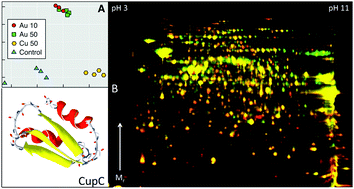
The metal-resistant β-proteobacterium Cupriavidus metallidurans drives gold (Au) biomineralisation and the (trans)formation of Au nuggets largely via unknown biochemical processes, ultimately leading to the reductive precipitation of mobile, toxic Au(I/III)-complexes. In this study proteomic responses of C. metallidurans CH34 to mobile, toxic Au(III)-chloride are investigated. Cells were grown in the presence of 10 and 50 μM Au(III)-chloride, 50 μM Cu(II)-chloride and without additional metals. Differentially expressed proteins were detected by difference gel electrophoresis and identified by liquid chromatography coupled mass spectrometry. Proteins that were more abundant in the presence of Au(III)-chloride are involved in a range of important cellular functions, e.g., metabolic activities, transcriptional regulation, efflux and metal transport. To identify Au-binding proteins, protein extracts were separated by native 2D gel electrophoresis and Au in protein spots was detected by laser absorption inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. A chaperon protein commonly understood to bind copper (Cu), CupC, was identified and shown to bind Au. This indicates that it forms part of a multi-metal detoxification system and suggests that similar/shared detoxification pathways for Au and Cu exist. Overall, this means that C. metallidurans CH34 is able to mollify the toxic effects of cytoplasmic Au(III) by sequestering this Au-species. This effect may in the future be used to develop CupC-based biosensing capabilities for the in-field detection of Au in exploration samples.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...