Design, synthesis and biological profiling of aryl piperazine based scaffolds for the management of androgen sensitive prostatic disorders†‡
Abstract
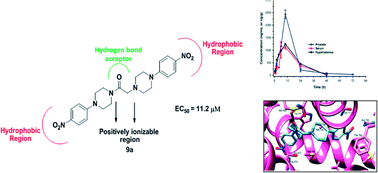
In the quest for novel scaffolds for the management of androgen sensitive prostatic disorders like prostate cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia, a series of twenty-six aryl/heteroaryl piperazine derivatives have been described. Three compounds, 8a, 8c and 9a, exhibited good activity profiles against an androgen sensitive prostate cancer cell line (LNCaP) with EC50 values of 9.8, 7.6 and 11.2 μM, respectively. These compounds caused a decrease in luciferase activity and a decline in PSA and Ca2+ levels, which are indicative of their anti-androgenic and α1A-adrenergic receptor blocking activities, respectively. Compound 9a reduced the prostate weight of rats (47%) and in pharmacokinetic analysis at 10 mg kg−1 it demonstrated an MRT of ∼14 h post dose, exhibiting high levels in prostate. Compound 9a docked in a similar orientation to hydroxyflutamide on an androgen receptor and showed strong π–π interactions. These findings reveal that compound 9a is a promising candidate for management of prostatic disorders with anti-androgenic and α1A-blocking activities.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...