Temperature-induced vesicle to micelle transition in cationic/cationic mixed surfactant systems†
Abstract
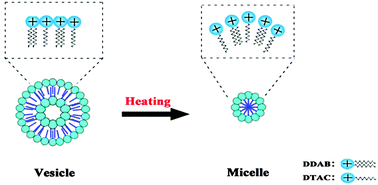
Temperature-induced vesicle to micelle transition (VMT), which has rarely been reported in cationic/cationic mixed surfactant systems, was systemically studied in a didodecyldimethylammonium bromide (DDAB)/dodecyltrimethylammonium chloride (DTAC) aqueous solution. We investigated the effect of temperature on DDAB/DTAC aqueous solutions by means of turbidity, conductivity, cryo-TEM, a UV-vis spectrophotometer, and a steady-state fluorescence spectrometer. It was found that increasing temperature could induce the transformation from the vesicle to the micelle in this cationic/cationic mixed surfactant system. The degree of transformation can be easily controlled by the operation temperature. Additionally, by adjusting the proportion of the mixed cationic/cationic systems and employing cationic surfactants with different chain-lengths, we were able to conclude that the hydrophobic tail length of the surfactant affects the aggregation behavior of cationic/cationic mixed surfactant systems as a function of temperature. It is universal to induce the transformation from the vesicle to the micelle by temperature in cationic/cationic mixed surfactant systems. A possible mechanism for the temperature-induced VMT was proposed based on the experimental results.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...