Graphene oxide-based Fe3O4 nanoparticles as a novel scaffold for the immobilization of porcine pancreatic lipase
Abstract
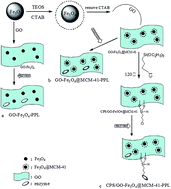
Nano- and hybrid materials have recently emerged as a new approach for improving enzyme activity and stability, and are suitable for commercial applications. In this paper, graphene oxide-based magnetic hybrids were prepared successfully. A chloropropyl-functionalized graphene oxide decorated with Fe3O4 nanoparticles was made, denoted as CPS/GO-Fe3O4@MCM-41. This was characterized by X-ray powder diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, vibrating sample magnetometry, thermogravimetry and N2 adsorption/desorption. Then, porcine pancreas lipase (PPL) was immobilized onto the graphene oxide-based magnetic nanoparticles via covalent bonding. The results show that the novel supporting material CPS/GO-Fe3O4@MCM-41 was the best for PPL immobilization compared to two other nanomaterials (GO-Fe3O4@MCM-41 and GO-Fe3O4). The supporting material CPS/GO-Fe3O4@MCM-41 exhibited enhanced immobilization efficiency (up to 98%), maximum relative activity (up to 97.9%), high stability and reusability (85% after 56 d and 87% after 10 cycles respectively, both at 30 °C). Additionally, it offered some other advantages, such as easy recycling and reuse, complying with the requirements of green chemistry. Therefore, it is proposed that CPS/GO-Fe3O4@MCM-41 provides a new approach for commercial applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...