Thermal decomposition based synthesis of Ag-In-S/ZnS quantum dots and their chlorotoxin-modified micelles for brain tumor cell targeting†
Abstract
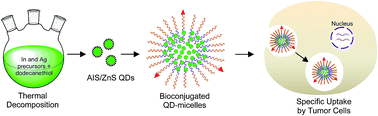
Cadmium-free silver-indium-sulfide (Ag-In-S or AIS) chalcopyrite quantum dots (QDs) as well as their core–shell structures (AIS/ZnS QDs) are being paid significant attention in biomedical applications because of their low toxicity and excellent optical properties. Here we report a simple and safe synthetic system to prepare high quality AIS and AIS/ZnS QDs using thermal decomposition. The synthetic system simply involves heating a mixture of silver acetate, indium acetate, and oleic acid in dodecanethiol at 170 °C to produce AIS QDs with a 13% quantum yield (QY). After ZnS shell growth, the produced AIS/ZnS QDs achieve a 41% QY. To facilitate phase transfer and bioconjugation of AIS/ZnS QDs for cellular imaging, these QDs were loaded into the core of PLGA–PEG (5kDa : 5kDa) based micelles to form AIS/ZnS QD-micelles. Cellular imaging studies showed that chlorotoxin-conjugated QD-micelles can be specifically internalized into U-87 brain tumor cells. This work discloses that the scalable synthesis of AIS/ZnS QDs and the facile surface/interface chemistry for phase transfer and bioconjugation of these QDs may open an avenue for the produced QD-micelles to be applied to the detection of endogenous targets expressed on brain tumor cells, or more broadly to cell- or tissue-based diagnosis and therapy.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...