Tin oxide nanoparticles from laser ablation encapsulated in a carbonaceous matrix – a negative electrode in lithium-ion battery applications
Abstract
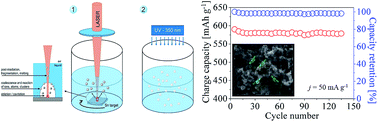
This report concerns carbonaceous electrodes doped with tin(II) oxide nanoparticles. Tin nanoparticles are obtained by pulsed laser ablation in water. Crystalline nanoparticles have been encapsulated in a carbonaceous matrix formed after pyrolysis of a mixture consisting of tin/tin(IV) oxide nanoparticles and gelatine. The obtained material is characterized by means of X-ray diffraction, selected area diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy and energy dispersive X-ray analysis. Battery charging/discharging tests exhibit a capacity of 580 mA h g−1 for current densities of 100 mA g−1. The cycling performance of the material suggests that the tested nanocomposite can be used as an anode for lithium-ion batteries.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...